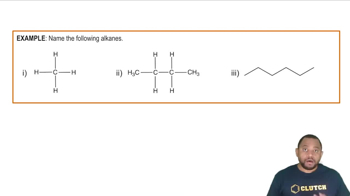
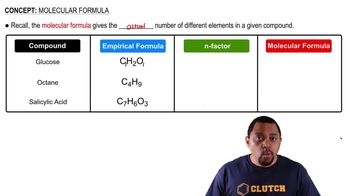
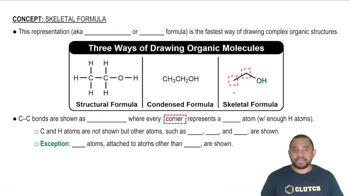
Lewis structures, condensed structural formulas, and skeletal structures are used to represent the structure of an organic compound. Each of the following compounds is shown in one of these representations. Convert each compound into the other two structural representations not shown.
(c)