Textbook Question
Give the structure and name of the cycloalkanes described.
(a) A compound whose molecular formula is C7H14 and contains a six-membered ring

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Give the structure and name of the cycloalkanes described.
(a) A compound whose molecular formula is C7H14 and contains a six-membered ring
Draw the condensed structural formula and skeletal structure of the saturated fatty acid with 16 carbon atoms. What is the name of this fatty acid?
Identify all of the functional groups in each of the following molecules:
(a)
Identify all of the functional groups in each of the following molecules:
(b)
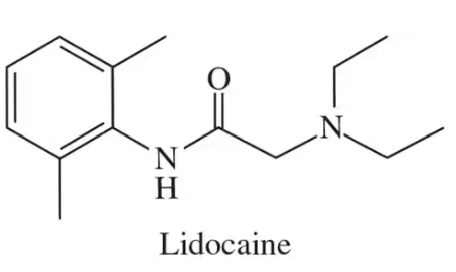
Name the four functional groups circled in the following molecule:
Write the condensed formula for each of the following molecules:
(b) 1,3-dichloro-3-methylheptane