Consider the following portion of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
5'CUU|AAA|CGA|GUU3'
c. Write the amino acid sequence if a mutation changes CGA to AGA. Is this likely to affect protein function?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
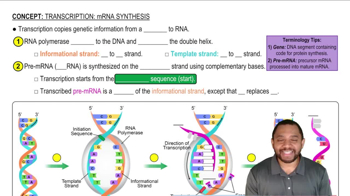
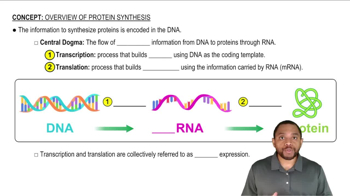
Consider the following portion of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
5'CUU|AAA|CGA|GUU3'
c. Write the amino acid sequence if a mutation changes CGA to AGA. Is this likely to affect protein function?
Consider the following portion of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
5'CUU|AAA|CGA|GUU3'
e. What happens to the protein sequence if an A is added to the beginning of the chain and the sequence changes to 5'ACU|UAA|ACG|AGU3'?
Consider the following portion of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
5'ACA|UCA|CGG|GUA3'
c. Write the amino acid sequence if a mutation changes CGG to GGG. Is this likely to affect protein function?
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
b. DNA polymerase
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
c. capsid
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
a. RNA