What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
b. alanine and valine

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
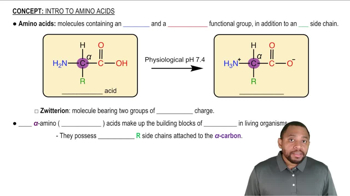

What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
b. alanine and valine
What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
a. lysine and glutamate
What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
b. leucine and isoleucine
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Peptide bonds join amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
d. Hydrogen bonding between amino acids in the same polypeptide gives a coiled shape to the protein.
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Hydrogen bonds form between adjacent segments of the backbone of the same protein to form a “folded-fan” structure.