When a protein folds into its tertiary structure, does the primary structure change? Explain.

What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
a. lysine and glutamate
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Amino Acid Side Chains
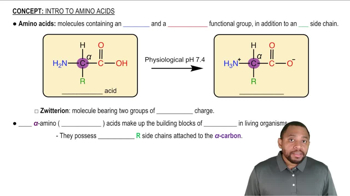
Ionic Interactions

Tertiary Structure of Proteins
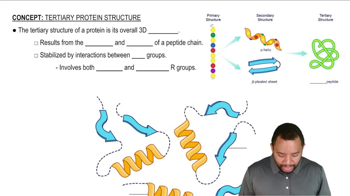
Describe the differences in the shape of an α helix and a β-pleated sheet.
What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
b. alanine and valine
What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
b. leucine and isoleucine
What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
d. glutamine and arginine
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Peptide bonds join amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
