What kind of interaction attracts the cofactor Mg2+ and ATP to each other? (Hint: Look at the structure of the phosphate group.)

Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor.
a. The structure of the inhibitor is similar to that of the substrate.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Competitive Inhibition

Noncompetitive Inhibition

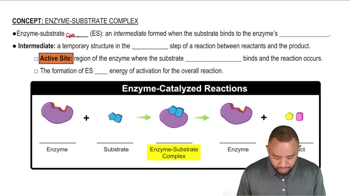
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
How would the following changes affect enzyme activity for an enzyme whose optimal conditions are normal body temperature and physiological pH?
a. raising the temperature from 37 °C to 60 °C
The enzyme urease functions in the body to catalyze the formation of ammonia and carbon dioxide from urea as shown:
Describe what effect the following changes would have on the rate of this reaction assuming a steady state has been reached:
a. adding excess urea
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor.
c. The inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site.
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor.
e. Adding more substrate to the reaction restores the enzyme activity.
Give the name and three-letter abbreviation for the amino acid described by each of the following:
a. the nonpolar amino acid with a sulfur atom in its side chain
