Three pairs of genes with two alleles each (A₁ and A₂, B₁ and B₂, and C₁ and C₂) control the height of a plant. The alleles of these genes have an additive relationship: Each copy of alleles A₁, B₁, and C₁ contributes 6 cm to plant height, and each copy of alleles A₂, B₂, and C₂ contributes 3 cm. What height is expected in the F₁ progeny of a cross between A₁A₁B₁B₁C₁C₁ and A₂A₂B₂B₂C₂C₂?
Ch. 19 - Genetic Analysis of Quantitative Traits

Sanders3rd EditionGenetic Analysis: An Integrated ApproachISBN: 9780135564172Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 19, Problem 8
What is a random sample, and why can a random sample be used to represent a population?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
A random sample is a subset of individuals chosen from a larger population where each individual has an equal chance of being selected. This ensures that the sample is unbiased and representative of the population.
To understand why a random sample can represent a population, consider that random sampling minimizes systematic bias. This means that the characteristics of the sample are more likely to reflect the diversity and distribution of traits in the entire population.
In genetics, random sampling is particularly important when studying traits or allele frequencies. By ensuring randomness, the sample can provide an accurate estimate of genetic variation within the population.
The principle of random sampling relies on the law of large numbers, which states that as the sample size increases, the sample's properties (e.g., mean, variance) will converge to those of the population.
In practice, random sampling is achieved using methods such as drawing lots, using random number generators, or other techniques that ensure each individual has an equal probability of selection.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Random Sampling
Random sampling is a technique used in statistics to select a subset of individuals from a larger population, where each individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This method helps to eliminate bias in the selection process, ensuring that the sample accurately reflects the diversity of the entire population.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Non-Random Mating
Population Representation
A random sample can represent a population because it captures the characteristics of the population without systematic bias. When a sample is randomly selected, it is more likely to include a variety of traits and attributes found in the larger group, allowing for generalizations and inferences to be made about the population as a whole.
Recommended video:
Guided course
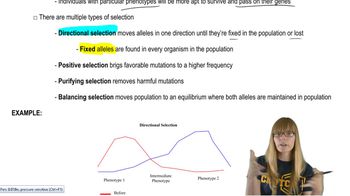
Natural Selection
Statistical Inference
Statistical inference is the process of using data from a random sample to make conclusions about a population. By analyzing the sample data, researchers can estimate population parameters, test hypotheses, and predict future trends, all while accounting for the inherent variability and uncertainty in the data.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Overview
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Provide a definition and an example for each of the following terms:
Polygenic inheritance
Textbook Question
Provide a definition and an example for each of the following terms:
Quantitative trait locus
Textbook Question
Provide a definition and an example for each of the following terms:
Threshold trait
Textbook Question
Why is heritability an important phenomenon in plant and animal agriculture?
Textbook Question
Three pairs of genes with two alleles each (A₁ and A₂, B₁ and B₂, and C₁ and C₂) control the height of a plant. The alleles of these genes have an additive relationship: Each copy of alleles A₁, B₁, and C₁ contributes 6 cm to plant height, and each copy of alleles A₂, B₂, and C₂ contributes 3 cm.
What are the expected heights of plants with each of the homozygous genotypes A₁A₁B₁B₁C₁C₁ and A₂A₂B₂B₂C₂C₂?
