Select one of the hereditary conditions from either the RUSP core conditions list or the RUSP list of secondary conditions and do some online research to find the following information:
The recommended treatment for those with the condition.

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 16 - Genomics: Genetics from a Whole-Genome Perspective
Ch. 16 - Genomics: Genetics from a Whole-Genome Perspective Problem 16b
Problem 16b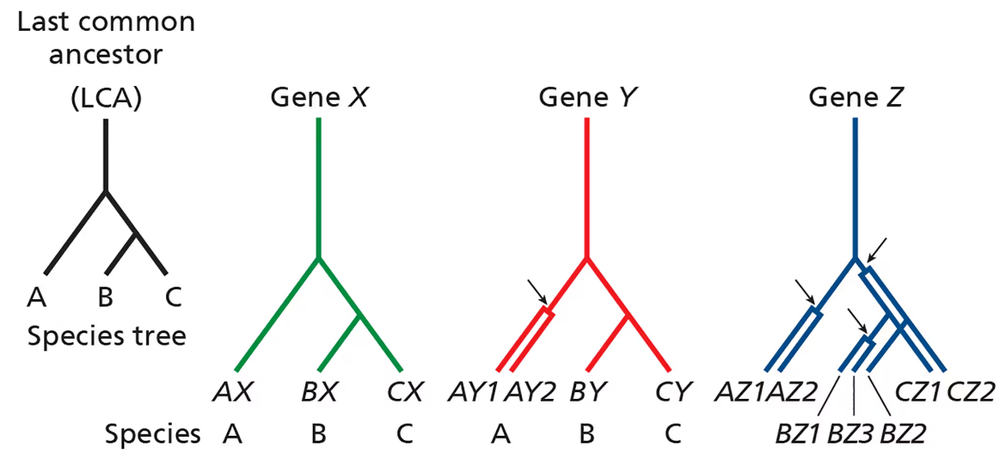
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Select one of the hereditary conditions from either the RUSP core conditions list or the RUSP list of secondary conditions and do some online research to find the following information:
The recommended treatment for those with the condition.
In the course of the Drosophila melanogaster genome project, the following genomic DNA sequences were obtained. Try to assemble the sequences into a single contig.
5' TTCCAGAACCGGCGAATGAAGCTGAAGAAG 3'
5' GAGCGGCAGATCAAGATCTGGTTCCAGAAC 3'
5' TGATCTGCCGCTCCGTCAGGCATAGCGCGT 3'
5' GGAGAATCGAGATGGCGCACGCGCTATGCC 3'
5' GGAGAATCGAGATGGCGCACGCGCTATGCC 3'
5' CCATCTCGATTCTCCGTCTGCGGGTCAGAT 3'
Go to the URL provided in Problem 14, and using the sequence you have just assembled, perform a blastn search in the 'Nucleotide collection (nr/nt)' database. Does the search produce sequences similar to your assembled sequence, and if so, what are they? Can you tell if your sequence is transcribed, and if it represents protein-coding sequence? Perform a tblastx search, first choosing the 'Nucleotide collection (nr/nt)' database and then limiting the search to human sequences by typing Homo sapiens in the organism box. Are homologous sequences found in the human genome? Annotate the assembled sequence.
Consider the phylogenetic trees below pertaining to three related species (A, B, and C) that share a common ancestor (last common ancestor, or LCA). The lineage leading to species A diverges before the divergence of species B and C.
For gene X, no gene duplications have occurred in any lineage, and each gene X is derived from the ancestral gene X via speciation events. Are genes AX, BX, and CX orthologous, paralogous, or homologous?
Consider the phylogenetic trees below pertaining to three related species (A, B, and C) that share a common ancestor (last common ancestor, or LCA). The lineage leading to species A diverges before the divergence of species B and C.
For gene Z, gene duplications have occurred in all species. Define orthology and paralogy relationships for the different Z genes.
You have isolated a gene that is important for the production of milk and wish to study its regulation. You examine the genomes of human, mouse, dog, chicken, pufferfish, and yeast and note that all genomes except yeast have an orthologous gene.
What does the existence of orthologous genes in chicken and pufferfish tell you about the function of this gene?
You have isolated a gene that is important for the production of milk and wish to study its regulation. You examine the genomes of human, mouse, dog, chicken, pufferfish, and yeast and note that all genomes except yeast have an orthologous gene.
How would you identify the regulatory elements important for the expression of your isolated gene in mammary glands?