Textbook Question
What is CODIS? Describe the four most important features of genetic markers used in this system.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


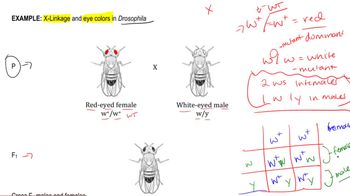
What is CODIS? Describe the four most important features of genetic markers used in this system.
Compare and contrast the terms Paternity Index (PI) and Combined Paternity Index (CPI). How does each contribute to paternity determination?
The human genome is 3×10⁹ bp in length.
How many fragments would be predicted to result from the complete digestion of the human genome with the following enzymes: Sau3A (˘GATC), BamHI (G˘GATCC), EcoRI (G˘AATTC), and NotI (GC˘GGCCGC)?