Using the genomic libraries, you wish to clone the human gene encoding myostatin, which is expressed only in muscle cells.
How frequently will a clone representing myostatin be found in the genomic library made from brain?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
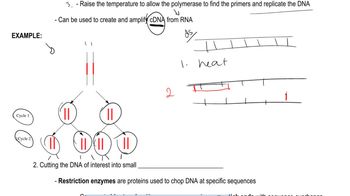

Using the genomic libraries, you wish to clone the human gene encoding myostatin, which is expressed only in muscle cells.
How frequently will a clone representing myostatin be found in the genomic library made from brain?
Using the genomic libraries, you wish to clone the human gene encoding myostatin, which is expressed only in muscle cells.
How frequently will a clone representing myostatin be found in the cDNA library made from muscle?
Using the genomic libraries, you wish to clone the human gene encoding myostatin, which is expressed only in muscle cells.
How frequently will a clone representing myostatin be found in the cDNA library made from brain?
A victim of murder is found to have scrapings containing skin cells under several of her fingernails. Genetic analysis confirms that the DNA isolated from these cells came from the same individual and does not match the DNA of the victim. The results shown below are for six CODIS STR markers from the crime scene DNA (from under the victim's fingernails and presumed to be the murderer's), and from three suspects (A, B, and C) who have been detained for questioning about the murder. Is there a failure to exclude any of the suspects? Explain.
A victim of murder is found to have scrapings containing skin cells under several of her fingernails. Genetic analysis confirms that the DNA isolated from these cells came from the same individual and does not match the DNA of the victim. The results shown below are for six CODIS STR markers from the crime scene DNA (from under the victim's fingernails and presumed to be the murderer's), and from three suspects (A, B, and C) who have been detained for questioning about the murder. Do the STR results exclude any of the three suspects? Explain.
The results shown are from a DNA test for four genes used in a paternity identification case. DNA for the mother (M) and her child (C) are shown along with DNA from two possible fathers, F1 and F2. Based on the exclusion principle, is either man excluded as the possible father? Explain.