Three independently assorting STR markers (A, B, and C) are used to assess the paternity of a colt recently born to a quarter horse mare. Blood samples are drawn from the mare, her colt, and three possible male sires (S₁, S₂, and S₃). DNA at each marker locus is amplified by PCR, and a DNA electrophoresis gel is run for each marker. Amplified DNA bands are visualized in each gel by ethidium bromide staining. Gel results are shown below for each marker. Evaluate the data and determine if any of the potential sires can be excluded. Explain the basis of exclusion, if any, in each case.

A major advance in the 1980s was the development of technology to synthesize short oligonucleotides. This work both facilitated DNA sequencing and led to the advent of the development of PCR. Recently, rapid advances have occurred in the technology to chemically synthesize DNA, and sequences up to 10 kb are now readily produced. As this process becomes more economical, how will it affect the gene-cloning approaches outlined in this chapter? In other words, what types of techniques does this new technology have potential to supplant, and what techniques will not be affected by it?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
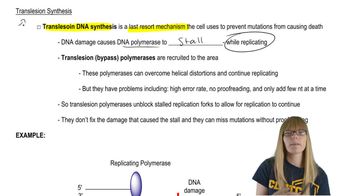
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
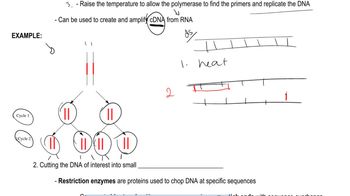
Gene Cloning Techniques

Three independently assorting STR markers (A, B, and C) are used to assess the paternity of a colt recently born to a quarter horse mare. Blood samples are drawn from the mare, her colt, and three possible male sires (S₁, S₂, and S₃). DNA at each marker locus is amplified by PCR, and a DNA electrophoresis gel is run for each marker. Amplified DNA bands are visualized in each gel by ethidium bromide staining. Gel results are shown below for each marker. Calculate the PI and CPI based on these STR markers, using the following population frequencies: A₁₂ = 0.12, A₁₀ = 0.18; B₁₈ = 0.08, B₁₂ = 0.17; C₁₆ = 0.11, C₁₄ = 0.20.
The bacteriophage lambda genome can exist in either a linear form or a circular form.
How many fragments will be formed by restriction enzyme digestion with XhoI alone, with XbaI alone, and with both XhoI and XbaI in the linear and circular forms of the lambda genome?
The bacteriophage lambda genome can exist in either a linear form or a circular form.
Diagram the resulting fragments as they would appear on an agarose gel after electrophoresis.
The restriction enzymes XhoI and SalI cut their specific sequences as shown below:
Can the sticky ends created by XhoI and SalI sites be ligated? If yes, can the resulting sequences be cleaved by either XhoI or SalI?
