Back
Back Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 14 - Analysis of Gene Function via Forward Genetics and Reverse Genetics
Ch. 14 - Analysis of Gene Function via Forward Genetics and Reverse GeneticsProblem C.9e
Go to the website http://www.cancer.gov and select 'Cancer Types' on the top menu bar. Scroll down to 'Breast Cancer' and click. Select 'Cases & Prevention' from the options. Click 'More information' and select 'BRCA Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing'. Use the information on this page to answer the following questions. As a special project, instead of selecting 'Breast Cancer' from the list of types of cancer, select another cancer you would like to know more about and produce a short summary of what you find.
Problem C.9a
Go to the website http://www.cancer.gov and select 'Cancer Types' on the top menu bar. Scroll down to 'Breast Cancer' and click. Select 'Cases & Prevention' from the options. Click 'More information' and select 'BRCA Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing'. Use the information on this page to answer the following questions. What are the approximate percentage increases in risk of having breast cancer and of having ovarian cancer for women inheriting harmful mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 compared with the risks in the general population?
Problem C.9d
Go to the website http://www.cancer.gov and select 'Cancer Types' on the top menu bar. Scroll down to 'Breast Cancer' and click. Select 'Cases & Prevention' from the options. Click 'More information' and select 'BRCA Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing'. Use the information on this page to answer the following questions. Are there measures a woman with a positive result can take to lessen her chances of developing cancer or to catch a cancer early in its development?
Problem C.9b
Go to the website http://www.cancer.gov and select 'Cancer Types' on the top menu bar. Scroll down to 'Breast Cancer' and click. Select 'Cases & Prevention' from the options. Click 'More information' and select 'BRCA Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing'. Use the information on this page to answer the following questions. What features of family history increase the likelihood that a woman will have a harmful mutation of BRCA1 or BRCA2?
Problem C.9c
Go to the website http://www.cancer.gov and select 'Cancer Types' on the top menu bar. Scroll down to 'Breast Cancer' and click. Select 'Cases & Prevention' from the options. Click 'More information' and select 'BRCA Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing'. Use the information on this page to answer the following questions. With regard to the results of genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, what is meant by a 'positive result'?
Problem 10
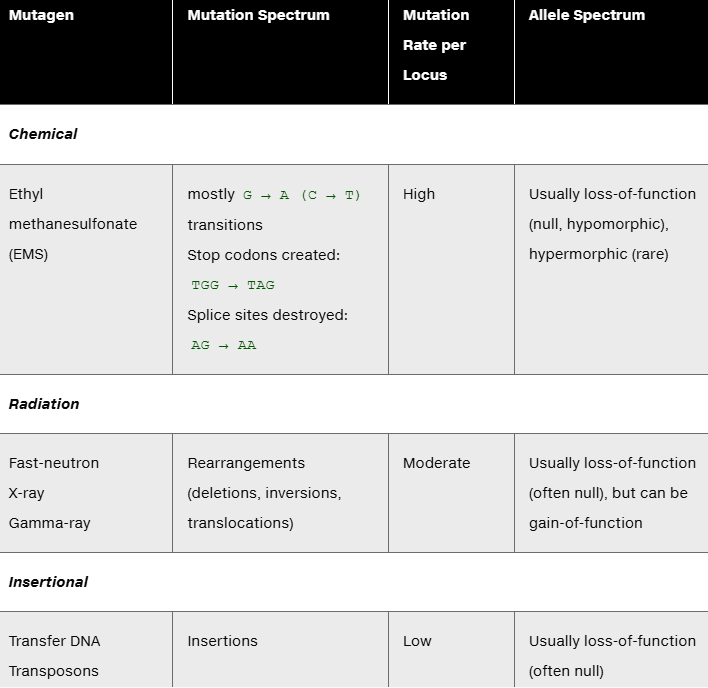
Discuss the advantages (and possible disadvantages) of the different mutagens in the following table:
Problem C.10
What kind of information will be made available by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)? What sort of role do you think TCGA information will play in cancer diagnosis and cancer treatment in the future?
Problem 11
You have identified a gene encoding the protein involved in the rate-limiting step in vitamin E biosynthesis. How would you create a transgenic plant producing large quantities of vitamin E in its seeds?
Problem C.11b
Go to the website http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and enter 'Lynch syndrome' in the Search box at the top of the page. From the list of options given, select '#120435—Lynch Syndrome.' Use the information you retrieve to answer the following questions. What genes are most commonly mutated in Lynch syndrome?
Problem C.11d
Go to the website http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and enter 'Lynch syndrome' in the Search box at the top of the page. From the list of options given, select '#120435—Lynch Syndrome.' Use the information you retrieve to answer the following questions. What are the approximate rates of cancer that develop in people carrying a mutation of one of these genes?
Problem C.11c
Go to the website http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and enter 'Lynch syndrome' in the Search box at the top of the page. From the list of options given, select '#120435—Lynch Syndrome.' Use the information you retrieve to answer the following questions. Provide a brief summary of the normal functions of the protein products of these genes.
Problem C.11a
Go to the website http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and enter 'Lynch syndrome' in the Search box at the top of the page. From the list of options given, select '#120435—Lynch Syndrome.' Use the information you retrieve to answer the following questions. There are two types of Lynch syndrome. What are they?
Problem 12
You have identified a recessive mutation that alters bristle patterning in Drosophila and have used recombinant DNA technology to identify a genomic clone that you believe harbors the gene. How would you demonstrate that your gene is on the genomic clone?
Problem C.12
Genetic counseling has not been discussed in this chapter, but it is a service provided by trained professional counselors who also have detailed knowledge of medical genetics, as described in Application Chapter A. Genetic counselors provide details about gene mutations and have knowledge of most of the details of diseases associated with genetic abnormalities. With regard to genetic testing to identify one's personal risk of cancer, what are the three or four topics you think are most important to be able to discuss with a genetic counselor?
Problem 13a
The CBF genes of Arabidopsis are induced by exposure of the plants to low temperature. How would you examine the temporal and spatial patterns of expression after induction by low temperature?
Problem 13b
The CBF genes of Arabidopsis are induced by exposure of the plants to low temperature. Can you design a method that would reveal these changes in gene expression in a way that a farmer could recognize them by observing plants growing in the field?
Problem 14a
When the S. cerevisiae genome was sequenced and surveyed for possible genes, only about 40% of those genes had been previously identified in forward genetic screens. This left about 60% of predicted genes with no known function, leading some to dub the genes fun (function unknown) genes. As an approach to understanding the function of a certain fun gene, you wish to create a loss-of-function allele. How will you accomplish this?
Problem 14b
When the S. cerevisiae genome was sequenced and surveyed for possible genes, only about 40% of those genes had been previously identified in forward genetic screens. This left about 60% of predicted genes with no known function, leading some to dub the genes fun (function unknown) genes. You wish to know the physical location of the encoded protein product. How will you obtain such information?
Problem 15
Translational fusions between a protein of interest and a reporter protein are used to determine the subcellular location of proteins in vivo. However, fusion to a reporter protein sometimes renders the protein of interest nonfunctional because the addition of the reporter protein interferes with proper protein folding, enzymatic activity, or protein–protein interactions. You have constructed a fusion between your protein of interest and a reporter gene. How will you show that the fusion protein retains its normal biological function?
Problem 16
In humans, Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by a mutation in the dystrophin gene, which resides on the X chromosome. How would you create a mouse model of this genetic disease?
Problem 17
How would you perform a genetic screen to identify genes directing Drosophila wing development? Once you have a collection of wing-development mutants, how would you analyze your mutagenesis to learn how many genes are represented and how many alleles of each gene? How would you discover whether the genes act in the same or different pathways, and if in the same pathway, how do you discover the order in which they act? How would you clone the genes?
Problem 18
In enhancer trapping experiments, a minimal promoter and a reporter gene are placed adjacent to the end of a transposon so that genomic enhancers adjacent to the insertion site can act to drive expression of the reporter gene. In a modification of this approach, a series of enhancers and a promoter can be placed at the end of a transposon so that transcription is activated from the transposon into adjacent genomic DNA. What types of mutations do you expect to be induced by such a transposon in a mutagenesis experiment?
Problem 19a
We designed a screen to identify conditional mutants of S. cerevisiae in which the secretory system was defective. Suppose we were successful in identifying 12 mutants.
Describe the crosses you would perform to determine the number of different genes represented by the 12 mutations.
Problem 19b
We designed a screen to identify conditional mutants of S. cerevisiae in which the secretory system was defective. Suppose we were successful in identifying 12 mutants.
Based on your knowledge of the genetic tools for studying baker's yeast, how would you clone the genes that are mutated in your respective yeast strains? What is an approach to cloning the human orthologs of the yeast genes?
Problem 20
How would you design a genetic screen to find genes involved in meiosis?
Problem 21a
The eyes of Drosophila develop from imaginal discs, groups of cells set aside in the fly embryo that differentiate into the adult structures during the pupal stage. Despite their importance in nature, eyes are dispensable for fruit fly life in the laboratory.
Devise a genetic screen to identify genes directing the development of the fly eye.
Problem 21b
The eyes of Drosophila develop from imaginal discs, groups of cells set aside in the fly embryo that differentiate into the adult structures during the pupal stage. Despite their importance in nature, eyes are dispensable for fruit fly life in the laboratory.
What complications might arise from genetic screens targeting an organ that differentiates late in development?
Problem 22
Given your knowledge of the genetic tools for studying Drosophila, outline a method by which you could clone the dunce and rutabaga genes identified by Seymour Benzer's laboratory in the genetic screen.
Problem 23a
Mutations in the CFTR gene result in cystic fibrosis in humans, a condition in which abnormal secretions are present in the lungs, pancreas, and sweat glands. The gene was mapped to a 500-kb region on chromosome 7 containing three candidate genes.
Using your knowledge of the disease symptoms, how would you distinguish between the candidate genes to decide which is most likely to encode the CFTR gene?
Problem 23b
Mutations in the CFTR gene result in cystic fibrosis in humans, a condition in which abnormal secretions are present in the lungs, pancreas, and sweat glands. The gene was mapped to a 500-kb region on chromosome 7 containing three candidate genes.
How would you prove that your chosen candidate is the CFTR gene?