A 20.0-mL sample of 0.115 M sulfurous acid (H2SO3) solution is titrated with 0.1014 M KOH. At what added volume of base solution does each equivalence point occur?
Ch.18 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium

Chapter 18, Problem 88
Phenolphthalein has a pKa of 9.7. It is colorless in its acid form and pink in its basic form. For each of the following pH values, determine whether [In-] > [HIn] and predict the color of a phenolphthalein solution: a. pH = 2.0 b. pH = 5.0 c. pH = 8.0 d. pH = 11.0
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1: Understand the relationship between pH, pKa, and the color change of phenolphthalein. Phenolphthalein changes color based on the ratio of its ionized form [In^-] to its non-ionized form [HIn].
insert step 2: Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pH = pKa + log([In^-]/[HIn]). This equation helps determine the ratio of [In^-] to [HIn] at a given pH.
insert step 3: For each pH value, compare it to the pKa of phenolphthalein (9.7) to determine the dominant form. If pH > pKa, [In^-] > [HIn]; if pH < pKa, [HIn] > [In^-].
insert step 4: a. For pH = 2.0, since 2.0 < 9.7, [HIn] > [In^-], so the solution is colorless.
insert step 5: b. For pH = 5.0, since 5.0 < 9.7, [HIn] > [In^-], so the solution is colorless.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pKa and Acid-Base Equilibrium
The pKa value of a weak acid indicates the pH at which the acid is half dissociated. It is a measure of the strength of the acid; lower pKa values correspond to stronger acids. In this context, phenolphthalein has a pKa of 9.7, meaning at pH values below this, the acid form (HIn) predominates, while above this pH, the basic form (In-) is favored.
Recommended video:
Guided course
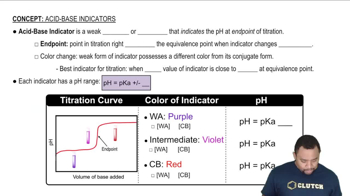
Acid-Base Indicators
Color Change of Indicators
Phenolphthalein is a pH indicator that changes color based on the acidity or basicity of the solution. It is colorless in its acidic form (HIn) and pink in its basic form (In-). Understanding the relationship between pH and the forms of the indicator is crucial for predicting the color of the solution at different pH levels.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid-Base Indicators
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates the pH of a solution to the pKa of an acid and the ratio of the concentrations of its deprotonated and protonated forms. It can be expressed as pH = pKa + log([In-]/[HIn]). This equation helps determine the predominant form of the indicator at a given pH, which is essential for predicting the color of the phenolphthalein solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Methyl red has a pKa of 5.0 and is red in its acid form and yellow in its basic form. If several drops of this indicator are placed in a 25.0-mL sample of 0.100 M HCl, what color will the solution appear? If 0.100 M NaOH is slowly added to the HCl sample, in what pH range will the indicator change color?
Textbook Question
Referring to Table 18.1, pick an indicator for use in the titration of each acid with a strong base. a. HF
Textbook Question
Referring to Table 17.1, pick an indicator for use in the titration of each base with a strong acid. a. CH3NH2
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations and expressions for Ksp for the dissolution of each ionic compound. a. BaSO4
