The following ball-and-stick molecular model is a representation of thalidomide, a drug that causes birth defects when taken by expectant mothers but is valuable for its use against leprosy. The lines indicate only the connections between atoms, not whether the bonds are single, double, or triple. 1Red = O, gray = C, blue = N, ivory = H.2 (a) What is the formula of thalidomide?
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure

All textbooks McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 38
Problem 38
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 38
Problem 38Chapter 8, Problem 38
What geometric arrangement of charge clouds do you expect for atoms that have the following number of charge clouds? (a) 3 (b) 5 (c) 2 (d) 6
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the number of charge clouds around the central atom. Charge clouds can include lone pairs and bonds (single, double, or triple).
Use the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory to predict the molecular geometry based on the number of charge clouds. This theory states that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion.
For 3 charge clouds, the electron pairs will arrange themselves in a trigonal planar shape to minimize repulsion.
For 5 charge clouds, the electron pairs will arrange themselves in a trigonal bipyramidal shape.
For 2 charge clouds, the electron pairs will arrange themselves in a linear shape, and for 6 charge clouds, they will arrange themselves in an octahedral shape.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. According to this theory, electron pairs, whether bonding or non-bonding, repel each other and will arrange themselves to minimize this repulsion, leading to specific geometric shapes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
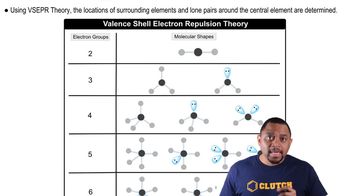
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR
Electron Clouds
In chemistry, 'charge clouds' refer to regions around an atom where electrons are likely to be found. These clouds can be formed by lone pairs of electrons or bonds between atoms. The arrangement of these clouds influences the molecular geometry, as they occupy space and affect the angles between bonds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
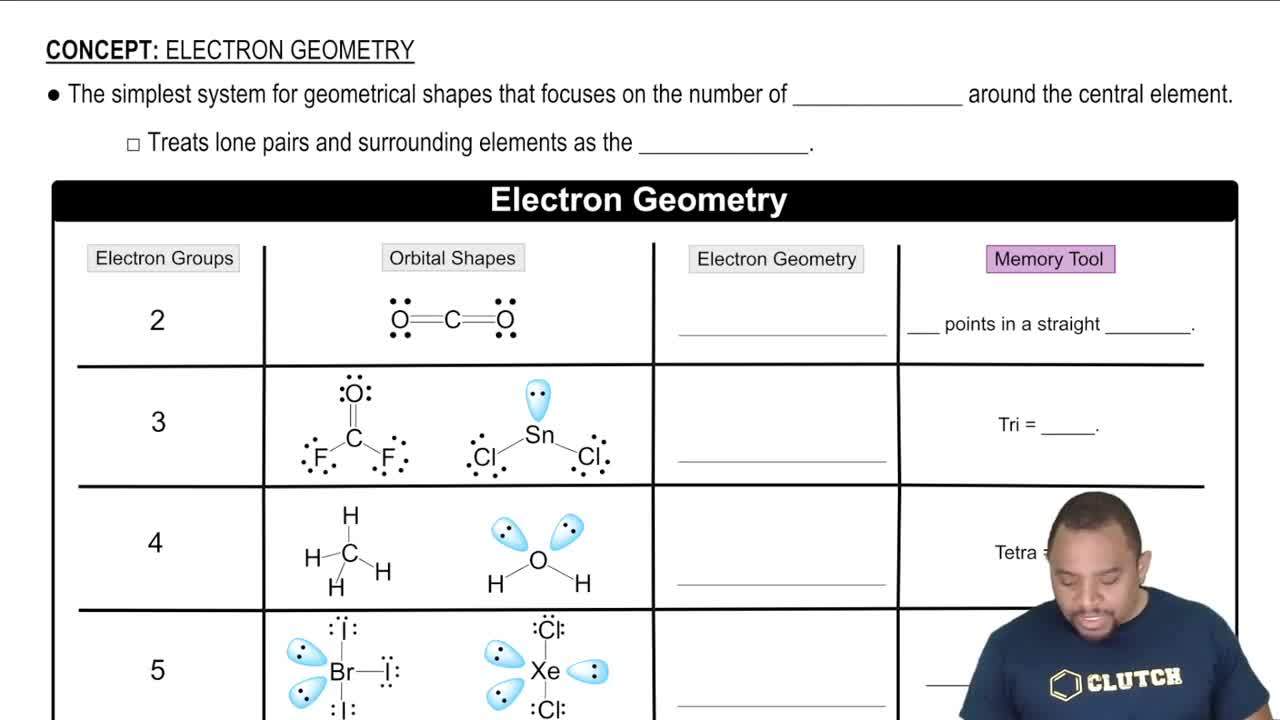
Electron Geometry
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry describes the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number of charge clouds around the central atom, which dictates the shape of the molecule, such as trigonal planar for three charge clouds, trigonal bipyramidal for five, linear for two, and octahedral for six.
Recommended video:
Guided course
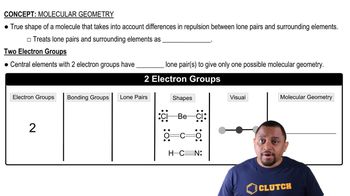
Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Ethyl acetate, CH3CO2CH2CH3, is commonly used as a solvent and nail-polish remover. Look at the following electrostatic potential map of ethyl acetate, and explain the observed polarity.
1
views
Textbook Question
Two dichloroethylene molecules with the same chemical formula 1C2H2Cl22, but different arrangements of atoms are shown. (b) Which form of dichloroethylene has a dipole moment of 2.39 D, and which has a dipole moment of 0.00 D?
1
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
What shape do you expect for molecules that meet the following descriptions? (a) A central atom with two lone pairs and three bonds to other atoms (b) A central atom with two lone pairs and two bonds to other atoms (c) A central atom with two lone pairs and four bonds to other atoms
Textbook Question
How many charge clouds are there around the central atom in molecules that have the following geometry?(a) Tetrahedral (b) Octahedral(c) Bent (d) Linear(e) Square pyramidal (f) Trigonal pyramidal
1
views
Textbook Question
What bond angles do you expect for each of the following? (d) The O¬B¬O angle in BO33-