Textbook Question
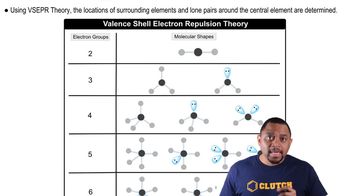
What geometric arrangement of charge clouds do you expect for atoms that have the following number of charge clouds? (a) 3 (b) 5 (c) 2 (d) 6
1
views

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 49
Problem 49 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance