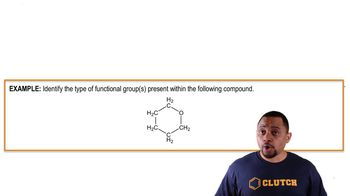
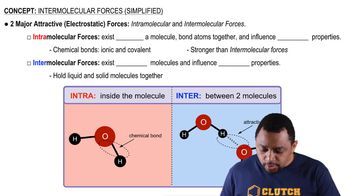
Textbook Question
The following diagram shows the potential energy of two atoms as a function of internuclear distance. Match the descriptions with the indicated letter on the plot.(a) Repulsive forces are high between the two atoms. (b) The two atoms neither exert attractive nor repulsive forces on one another.(c) The attractive forces between atoms are maximized, resulting in the lowest energy state.(d) Attractive forces between atoms are present but are not at maximum strength.