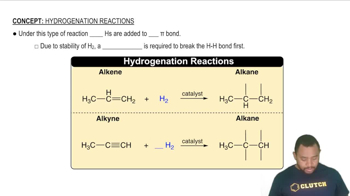
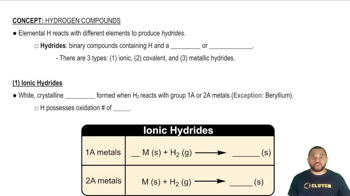
Hydride Ion (H-)
H- is known as a hydride ion, which occurs when hydrogen gains an extra electron, resulting in a negative charge. This form of hydrogen is typically found in ionic compounds with metals, where it acts as a reducing agent. Recognizing the presence of H- is important for understanding the reactivity and bonding in certain compounds.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance