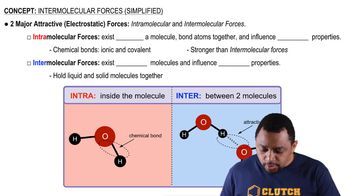
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction or repulsion between molecules and play a crucial role in determining physical properties such as boiling and melting points. HCl, being a polar molecule, exhibits dipole-dipole interactions, while CaH2, an ionic compound, has strong ionic bonds. TiH1.7, with its metallic bonding, has delocalized electrons contributing to its unique properties. The strength and type of these forces directly affect the compounds' states at room temperature.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance