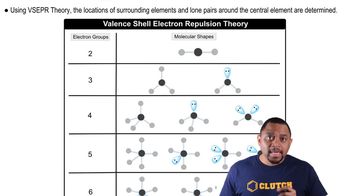
Hybridization
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that can accommodate bonding. In the case of AsH3, the arsenic atom undergoes sp3 hybridization, which involves the mixing of one s orbital and three p orbitals, resulting in four equivalent sp3 hybrid orbitals that facilitate the formation of bonds with hydrogen atoms.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance