Describe the intermediate that is thought to form in the addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene, using cyclohexene as the alkene in your description.
Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
All textbooks Brown 15th Edition
Brown 15th Edition Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Problem 46a
Problem 46a
 Brown 15th Edition
Brown 15th Edition Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Problem 46a
Problem 46aChapter 24, Problem 46a
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
a. butanoic acid and methanol
Name the compound in each case.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the functional groups in the reactants: Butanoic acid contains a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) and methanol contains an alcohol group (-OH).
Understand the mechanism of a condensation reaction: In this case, it involves the formation of an ester linkage. The -OH from the carboxylic acid group of butanoic acid will react with the -H from the -OH group of methanol, releasing a molecule of water (H2O).
Write the structural formula for both reactants: Butanoic acid is CH3CH2CH2COOH and methanol is CH3OH.
Combine the reactants to form the ester: Remove water (H2O) from the reactants and link the remaining parts. The oxygen from the methanol attaches to the carbonyl carbon of butanoic acid.
Name the resulting compound: The ester formed from butanoic acid and methanol is called methyl butanoate, following the nomenclature rules for esters (alkyl group from alcohol + name of acid with 'ic' replaced by 'ate').

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Condensation Reactions
Condensation reactions involve the combination of two molecules to form a larger molecule, accompanied by the loss of a small molecule, often water. In organic chemistry, these reactions frequently occur between carboxylic acids and alcohols, resulting in the formation of esters. Understanding this process is crucial for predicting the products of the reaction between butanoic acid and methanol.
Recommended video:
Guided course
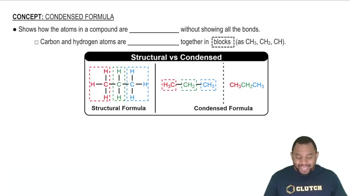
Condensed Formula
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In this case, butanoic acid contains a carboxylic acid group (-COOH), while methanol contains a hydroxyl group (-OH). Recognizing these functional groups helps in identifying the nature of the reaction and the resulting compound.
Recommended video:
Guided course
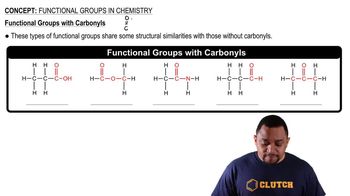
Carbonyl Functional Groups
IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method for naming chemical compounds based on their structure and functional groups. For the product formed from butanoic acid and methanol, the name will reflect the ester formed, which is butyl butanoate. Familiarity with IUPAC rules is essential for accurately naming the compounds resulting from chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
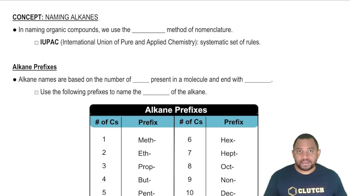
Rules for Naming Alkanes
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
a. benzoic acid and ethanol
Name the compound in each case.
Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
c. acetic acid and phenol.
Name the compound in each case.
Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
b. benzoic acid and 2-propanol
Name the compound in each case.
Textbook Question
Write a balanced chemical equation using condensed structural formulas for the saponification (base hydrolysis) of
a. methyl propionate
Textbook Question
Write a balanced chemical equation using condensed structural formulas for the saponification (base hydrolysis) of
b. phenyl acetate.