Textbook Question
a. What functional group characterizes an alcohol?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
a. What functional group characterizes an alcohol?
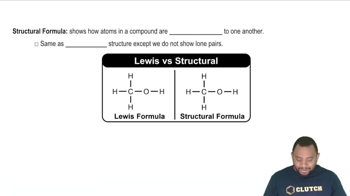
b. Write a structural formula for 1-pentanol.
All the structures shown here have the molecular formula C8H18. Which structures are the same molecule? (Hint: One way to answer this question is to determine the chemical name for each structure.)
How many isomers are there of n-pentanol?
Suppose a scientist repeats the Millikan oil-drop experiment but reports the charges on the drops using an unusual (and imaginary) unit called the warmomb (wa). The scientist obtains the following data for four of the drops: Droplet Calculated Charge (wa) A 3.84⨉10−8 B 4.80⨉10−8 C 2.88⨉10−8 D 8.64⨉10−8 (a) If all the droplets were the same size, which would fall most slowly through the apparatus?