Textbook Question
a. What elements are contained in hydrocarbons?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
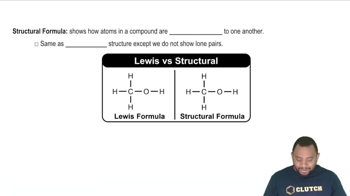
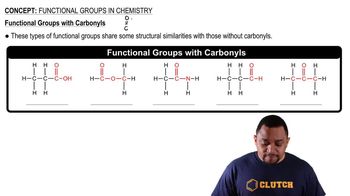
a. What elements are contained in hydrocarbons?
d. What is the empirical formula for octane?
a. What functional group characterizes an alcohol?
All the structures shown here have the molecular formula C8H18. Which structures are the same molecule? (Hint: One way to answer this question is to determine the chemical name for each structure.)