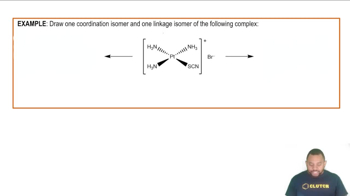
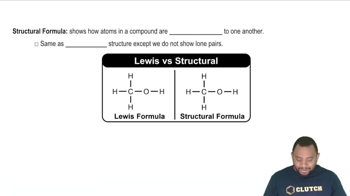
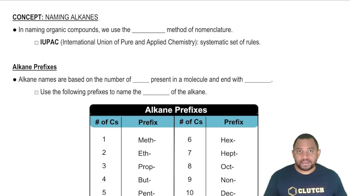
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations of atoms. In the case of C8H18, there are several isomers, including straight-chain and branched forms, which can exhibit different physical and chemical properties despite having the same molecular formula.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance