Using data from Appendix D, calculate 3OH-4 and pH for each of the following solutions: (b) 0.035 M Na2S
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 86b
Pyridinium bromide 1C5H5NHBr2 is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into C5H5NH+ and Br-. An aqueous solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. (b) Using Appendix D, calculate the Ka for pyridinium bromide.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the species in solution: Pyridinium bromide dissociates into \( \text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{NH}^+ \) and \( \text{Br}^- \). The \( \text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{NH}^+ \) acts as a weak acid in water.
Write the equilibrium expression for the dissociation of \( \text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{NH}^+ \): \( \text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{NH}^+ + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightleftharpoons \text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{N} + \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \).
Use the pH to find the concentration of \( \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \): \( \text{[H}_3\text{O}^+] = 10^{-\text{pH}} \).
Assume that the initial concentration of \( \text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{NH}^+ \) is equal to the concentration of \( \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \) at equilibrium, since the solution is dilute.
Calculate \( K_a \) using the expression \( K_a = \frac{[\text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{N}][\text{H}_3\text{O}^+]}{[\text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{NH}^+]} \), where the concentrations of \( \text{C}_5\text{H}_5\text{N} \) and \( \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \) are equal to the \( \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \) concentration found from the pH.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Strong Electrolytes
Strong electrolytes are substances that completely dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. This means that they produce a high concentration of ions in solution, which is crucial for understanding their behavior in chemical reactions and their effect on properties like conductivity and pH.
Recommended video:
Guided course
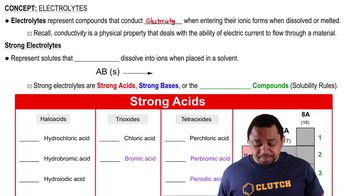
Electrolytes and Strong Acids
pH and Acidity
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, indicating its acidity or basicity. A lower pH value, such as 2.95, signifies a more acidic solution, which is relevant for calculating the dissociation of weak acids and their equilibrium constants, such as Ka.
Recommended video:
Guided course
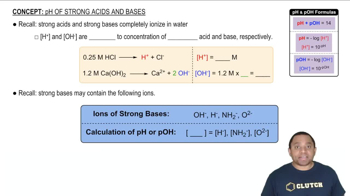
pH of Strong Acids and Bases
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) quantifies the strength of an acid in solution, representing the equilibrium between the undissociated acid and its ions. It is calculated using the concentrations of the products and reactants at equilibrium, and is essential for understanding the behavior of weak acids in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
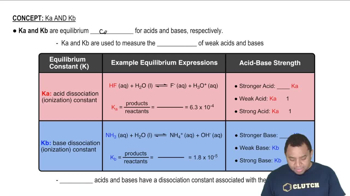
Characteristics of Ka and Kb
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Pyridinium bromide 1C5H5NHBr2 is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into C5H5NH+ and Br-. An aqueous solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. (a) Write out the reaction that leads to this acidic pH.
Textbook Question
Pyridinium bromide 1C5H5NHBr2 is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into C5H5NH+ and Br-. An aqueous solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. (c) A solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. What is the concentration of the pyridinium cation at equilibrium, in units of molarity?
Textbook Question
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following compounds are acidic, basic, or neutral: (c) Na2CO3
Textbook Question
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following substances are acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) AlCl3
