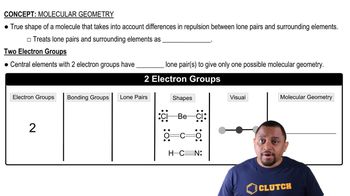
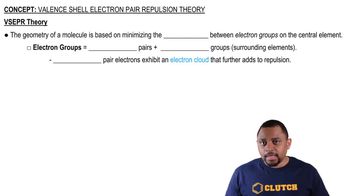
Textbook Question
(b) Imagine that you could hold two atoms that are bonded together, twist them, and not change the bond length. Would it be easier to twist (rotate) around a single s bond or around a double 1s plus p2 bond, or would they be the same?