Textbook Question
(c) Which is generally stronger, a s bond or a p bond? Explain.


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

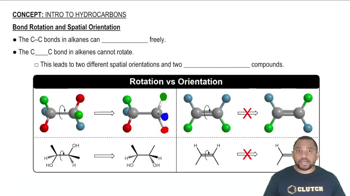
(c) Which is generally stronger, a s bond or a p bond? Explain.
(d) Can two s orbitals combine to form a p bond? Explain.
(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane (CH3Cl), chloroethene (C2H3Cl), and chloroethyne (C2HCl).
(b) What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in each molecule?