Textbook Question
(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane (CH3Cl), chloroethene (C2H3Cl), and chloroethyne (C2HCl).

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
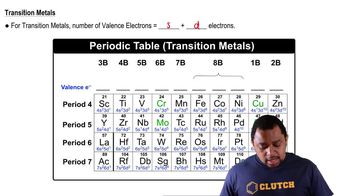

(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane (CH3Cl), chloroethene (C2H3Cl), and chloroethyne (C2HCl).
(b) What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in each molecule?
Benzaldehyde, C7H6O, is a fragrant substance responsible for the aroma of almonds. Its Lewis structure is
(a) What is the hybridization at each of the carbon atoms of the molecule?
Ethyl acetate, C4H8O2, is a fragrant substance used both as a solvent and as an aroma enhancer. Its Lewis structure is
(c) How many of the valence electrons are used to make s bonds in the molecule?
Ethyl acetate, C4H8O2, is a fragrant substance used both as a solvent and as an aroma enhancer. Its Lewis structure is
(e) How many valence electrons remain in nonbonding pairs in the molecule?