The maximum allowable concentration of lead in drinking water is 9.0 ppb. (a) Calculate the molarity of lead in a 9.0-ppb solution.
Ch.13 - Properties of Solutions

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 13, Problem 98a
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (a) molality,
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by understanding the relationship between molarity and molality. Molarity (M) is moles of solute per liter of solution, while molality (m) is moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
Calculate the mass of the solution using its density. Use the formula: \( \text{mass of solution} = \text{density} \times \text{volume} \). Assume 1 L of solution for simplicity, so the mass of the solution is \( 0.826 \text{ g/cm}^3 \times 1000 \text{ cm}^3 \).
Determine the moles of LiBr in the solution. Since the solution is 1.80 M, there are 1.80 moles of LiBr in 1 L of solution.
Calculate the mass of LiBr using its molar mass. The molar mass of LiBr is approximately 86.85 g/mol, so the mass of LiBr is \( 1.80 \text{ moles} \times 86.85 \text{ g/mol} \).
Find the mass of the solvent (acetonitrile) by subtracting the mass of LiBr from the total mass of the solution. Finally, calculate the molality using the formula: \( \text{molality} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{kilograms of solvent}} \).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molarity
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is commonly used in chemistry to express the concentration of a solution. In this case, the 1.80 M LiBr solution indicates that there are 1.80 moles of lithium bromide dissolved in one liter of acetonitrile.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molarity
Molality
Molality is another measure of concentration, defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. Unlike molarity, which depends on the volume of the solution, molality is based on the mass of the solvent, making it useful for temperature-dependent calculations. To convert from molarity to molality, the mass of the solvent must be known.
Recommended video:
Guided course
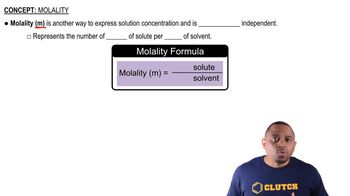
Molality
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume and is a critical property in calculating concentrations. In this context, the density of the solution (0.826 g/cm³) allows for the conversion between the mass of the solution and its volume. This information is essential for determining the mass of the solvent when calculating molality from the given molarity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
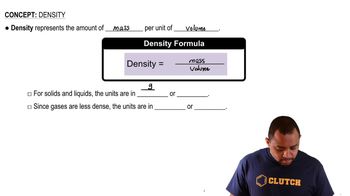
Density Concepts
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
The maximum allowable concentration of lead in drinking water is 9.0 ppb. (b) How many grams of lead are in a swimming pool containing 9.0 ppb lead in 60 m3 of water?
Textbook Question
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (b) mole fraction of LiBr,
1
views
Textbook Question
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (c) mass percentage of CH3CN.
Textbook Question
A 'canned heat' product used to warm buffet dishes consists of a homogeneous mixture of ethanol 1C2H5OH2 andparaffin, which has an average formula of C24H50. Whatmass of C2H5OH should be added to 620 kg of the paraffinto produce 8 torr of ethanol vapor pressure at 35 °C? Thevapor pressure of pure ethanol at 35 °C is 100 torr.
