The presence of the radioactive gas radon (Rn) in well water presents a possible health hazard in parts of the United States. (b) A sample consisting of various gases contains 3.5 × 10-6 mole fraction of radon. This gas at a total pressure of 32 atm is shaken with water at 30 °C. Calculate the molar concentration of radon in the water.
Ch.13 - Properties of Solutions

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 13, Problem 97a
The maximum allowable concentration of lead in drinking water is 9.0 ppb. (a) Calculate the molarity of lead in a 9.0-ppb solution.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that 'ppb' stands for 'parts per billion', which means 9.0 grams of lead per 1 billion grams of solution.
Convert the mass of lead from grams to moles using the molar mass of lead (Pb), which is approximately 207.2 g/mol. Use the formula: \( \text{moles of Pb} = \frac{\text{mass of Pb in grams}}{\text{molar mass of Pb}} \).
Assume the density of the solution is similar to that of water, approximately 1 g/mL, to convert the mass of the solution to volume. Since 1 billion grams is equivalent to 1 million liters, use this volume for the solution.
Calculate the molarity of the lead solution using the formula: \( \text{Molarity (M)} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{liters of solution}} \).
Substitute the values obtained from the previous steps into the molarity formula to find the molarity of lead in the solution.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Parts Per Billion (ppb)
Parts per billion (ppb) is a unit of measurement used to describe the concentration of a substance in a solution. It indicates how many parts of a substance are present in one billion parts of the total solution. In the context of drinking water, a concentration of 9.0 ppb means there are 9 micrograms of lead in every liter of water.
Recommended video:
Guided course
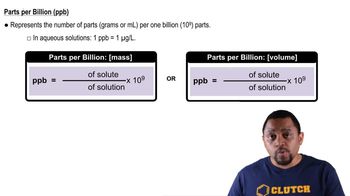
Parts per Billion (ppb)
Molarity
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L). To calculate molarity, one must know the mass of the solute, its molar mass, and the volume of the solution in liters. This concept is essential for converting ppb to molarity.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molarity
Molar Mass of Lead
The molar mass of lead (Pb) is approximately 207.2 g/mol. This value is crucial for converting the mass of lead in a solution (in grams) to moles, which is necessary for calculating molarity. Knowing the molar mass allows for accurate conversions between mass and the number of moles, facilitating the determination of concentration in chemical solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molar Mass Concept
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The maximum allowable concentration of lead in drinking water is 9.0 ppb. (b) How many grams of lead are in a swimming pool containing 9.0 ppb lead in 60 m3 of water?
Textbook Question
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (a) molality,
Textbook Question
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (b) mole fraction of LiBr,
1
views
