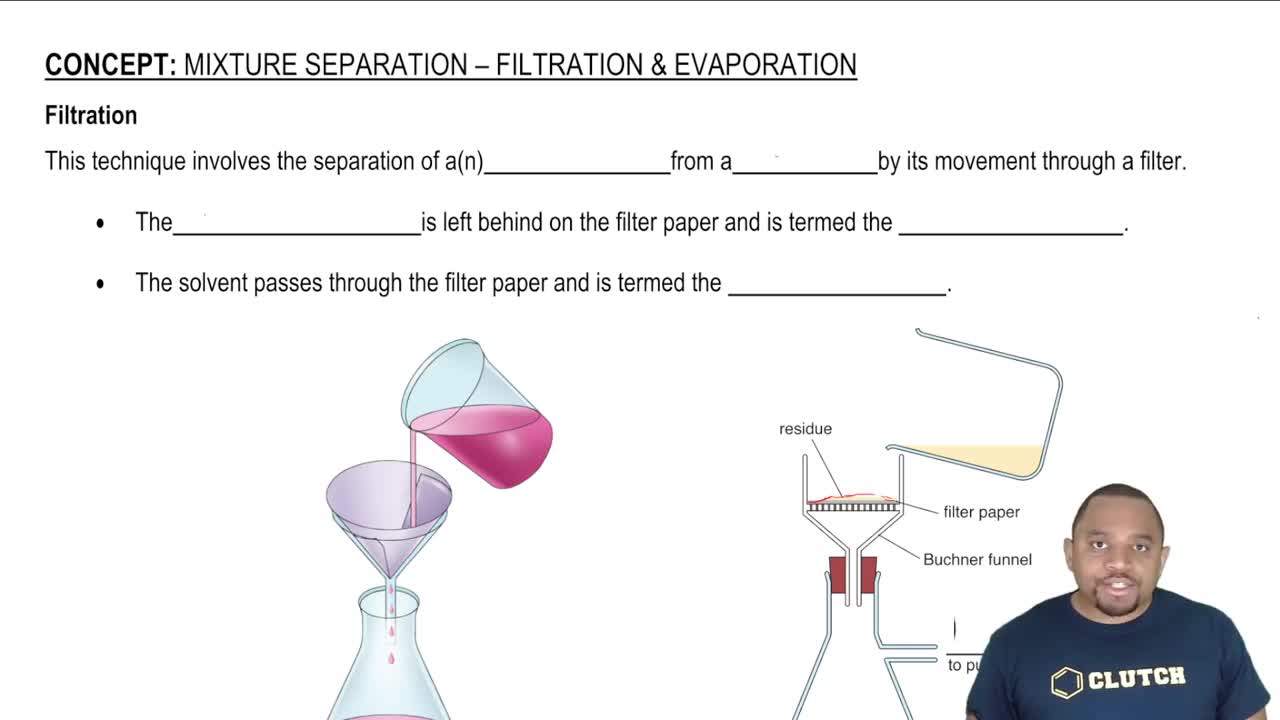
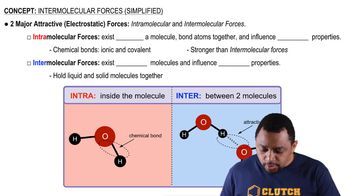
Textbook Question
The boiling points, surface tensions, and viscosities of water and several alcohols are as shown below: (b) How do you explain the fact that propanol and ethylene glycol have similar molecular weights (60 versus 62 amu), yet the viscosity of ethylene glycol is more than 10 times larger than propa- nol?