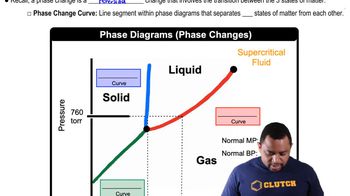
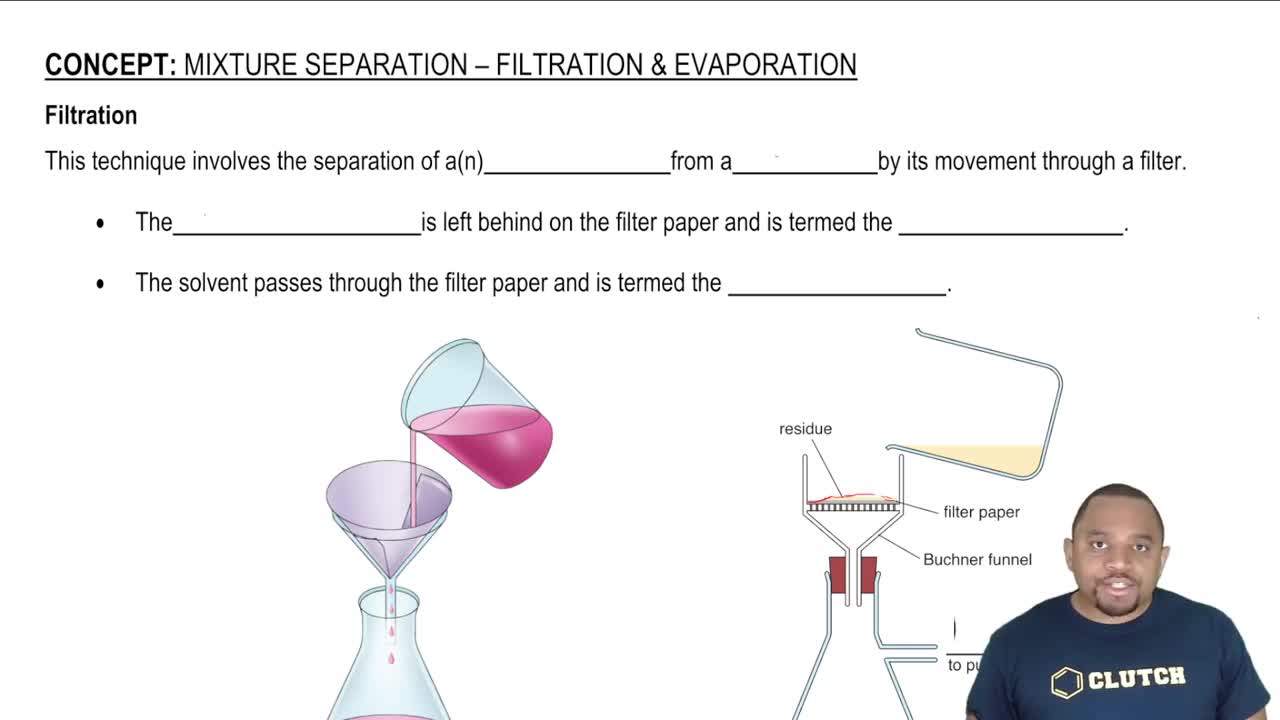
Textbook Question
Liquids can interact with flat surfaces just as they can with capillary tubes; the cohesive forces within the liquid can be stronger or weaker than the adhesive forces between liquid and surface:
(b) Which of these diagrams, i or ii, rep- resents what happens when water is on a nonpolar surface?