For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(d) [Cu(en)2]2+ (square planar)

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.122
Problem 21.122 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(d) [Cu(en)2]2+ (square planar)
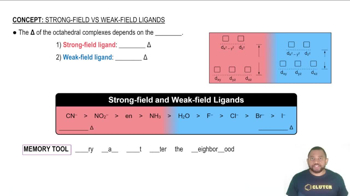
The [Cr(H2O)6]3+ ion is violet, and [Cr(CN)6]3- is yellow. Explain this difference using crystal field theory. Use the colors to order H2O and CN- in the spectrochemical series.
Draw the structures of all possible diastereoisomers of an octahedral complex with the formula MA2B2C2. Which of the diastereoisomers, if any, can exist as enantiomers?
Although Cl- is a weak-field ligand and CN- is a strong field ligand, [CrCl6]3- and [Cr(CN)6]3- exhibit approximately the same amount of paramagnetism. Explain.
The Ni2+(aq) cation is green, but Zn2+(aq) is colorless. Explain.
The glycinate anion, gly-= NH2CH2CO2 -, bonds to metal ions through the N atom and one of the O atoms. Using to represent gly-, sketch the structures of the four stereoisomers of Co(gly)3.