Draw the structures of all possible diastereoisomers of an octahedral complex with the formula MA2B2C2. Which of the diastereoisomers, if any, can exist as enantiomers?

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.108
Problem 21.108The Ni2+(aq) cation is green, but Zn2+(aq) is colorless. Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Transition Metal Ions and Color
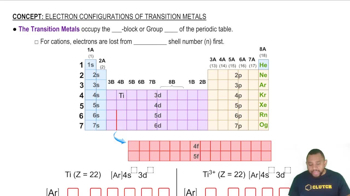
Electronic Configuration of Ions

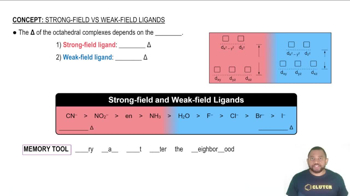
Ligand Field Theory
Predict the crystal field energy-level diagram for a square pyramidal ML5 complex that has two ligands along the axes but only one ligand along the z axis. Your diagram should be intermediate between those for an octahedral ML6 complex and a square planar ML4 complex.
Although Cl- is a weak-field ligand and CN- is a strong field ligand, [CrCl6]3- and [Cr(CN)6]3- exhibit approximately the same amount of paramagnetism. Explain.
The glycinate anion, gly-= NH2CH2CO2 -, bonds to metal ions through the N atom and one of the O atoms. Using to represent gly-, sketch the structures of the four stereoisomers of Co(gly)3.
What is the oxidation state of the metal in each of the complexes?
a. [Ni(CN)5]3–
b. Ni(CO)4
c. [Co(en)2(H2O)Br]2+
d. [Cu(H2O)2(C2O4)2]2–
e. Co(NH3)3(NO2)3
Explain why [CoCl4]2- (blue) and [Co(H2O)6]2+ (pink) have different colors. Which complex has its absorption bands at longer wavelengths?