Fill in the gaps in the following table: Symbol 59Co3+ Protons 34 76 80 Neutrons 46 116 120 Electrons 36 78 Net charge 2+
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 58d
Using the periodic table, predict the charge of the most stable ion of the following elements: d. Br
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the group number of bromine (Br) in the periodic table. Bromine is in Group 17, also known as the halogens.
Understand that elements in Group 17 typically gain one electron to achieve a full outer shell, similar to the nearest noble gas configuration.
Recognize that gaining one electron results in a negative charge. Therefore, the most stable ion of bromine will have a charge of -1.
Write the electron configuration of bromine: [Ar] 3d^{10} 4s^{2} 4p^{5}.
By gaining one electron, bromine achieves the electron configuration of krypton: [Ar] 3d^{10} 4s^{2} 4p^{6}, resulting in a Br^- ion.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Periodic Table and Group Trends
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number and properties. Elements in the same group (column) exhibit similar chemical behaviors, including their tendency to gain or lose electrons. For example, halogens like bromine (Br) are in Group 17 and typically gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration, resulting in a charge of -1.
Recommended video:
Guided course
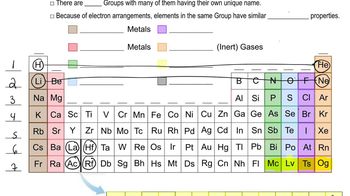
Periodic Table: Group Names
Ion Formation and Stability
Ions are charged particles formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. The stability of an ion is often related to achieving a noble gas electron configuration, which is energetically favorable. For bromine, gaining one electron to form Br- allows it to mimic the electron configuration of the nearest noble gas, krypton, thus making it a stable ion.
Recommended video:
Guided course
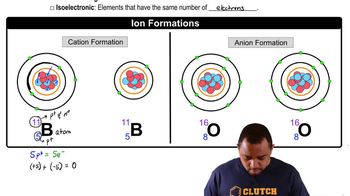
Ion Formation
Electronegativity and Electron Affinity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons, while electron affinity refers to the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom. Bromine has high electronegativity and a significant electron affinity, indicating a strong tendency to gain an electron and form a stable anion (Br-), which is crucial for predicting its charge.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Electron Affinity
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the gaps in the following table:
Symbol 31P3-
Protons 34 50
Neutrons 45 69 118
Electrons 46 76
Net charge 2- 3+
Textbook Question
Each of the following elements is capable of forming an ion in chemical reactions. By referring to the periodic table, predict the charge of the most stable ion of each: c. K
Textbook Question
Using the periodic table, predict the charge of the most stable ion of the following elements: e. Se
Textbook Question
Using the periodic table to guide you, predict the chemical formula and name of the compound formed by the following elements: (a) Ga and F (b) Li and H
Textbook Question
Using the periodic table to guide you, predict the chemical formula and name of the compound formed by the following elements: (c) Al and I
