The Ni2+(aq) cation is green, but Zn2+(aq) is colorless. Explain.
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry

All textbooks McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.119
Problem 21.119
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.119
Problem 21.119Chapter 21, Problem 21.119
Explain why [CoCl4]2- (blue) and [Co(H2O)6]2+ (pink) have different colors. Which complex has its absorption bands at longer wavelengths?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
1. The color of a complex ion depends on the difference in energy between the d orbitals. This difference is determined by the ligands that are attached to the metal ion. In this case, we have two different ligands: Cl- and H2O.
2. The ligand Cl- is a stronger field ligand than H2O. This means that it causes a larger splitting of the d orbitals in the Co ion. The larger the splitting, the higher the energy of the light that is absorbed (and thus, the shorter the wavelength).
3. Therefore, the [CoCl4]2- complex absorbs light of higher energy (shorter wavelength) than the [Co(H2O)6]2+ complex. This is why they have different colors: [CoCl4]2- appears blue because it absorbs light in the orange-red part of the spectrum, while [Co(H2O)6]2+ appears pink because it absorbs light in the green part of the spectrum.
4. The complex that has its absorption bands at longer wavelengths is the one that absorbs lower energy light. In this case, that would be the [Co(H2O)6]2+ complex.
5. Remember that the color we see is the color that is not absorbed by the complex. So, a complex that absorbs green light will appear red, and a complex that absorbs orange-red light will appear blue.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory explains how the arrangement of ligands around a central metal ion affects the energy levels of the d-orbitals. In octahedral complexes, such as [Co(H2O)6]2+, the d-orbitals split into two energy levels due to ligand interactions. This splitting influences the color observed, as different wavelengths of light are absorbed to promote electrons to higher energy levels.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The study of ligand-metal interactions helped to form Ligand Field Theory which combines CFT with MO Theory.
Ligand Field Strength
Ligand field strength refers to the ability of a ligand to influence the energy of the d-orbitals in a metal complex. Strong field ligands, like water in [Co(H2O)6]2+, cause greater splitting of the d-orbitals, leading to higher energy transitions and different colors. In contrast, weaker field ligands, like chloride in [CoCl4]2-, result in smaller splitting and different absorption characteristics.
Recommended video:
Guided course
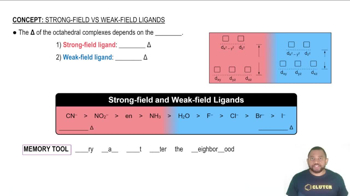
Strong-Field Ligands result in a large Δ and Weak-Field Ligands result in a small Δ.
Color and Absorption
The color of a complex ion is determined by the wavelengths of light it absorbs. When a complex absorbs light, the remaining light is what we perceive as its color. The complex that absorbs light at longer wavelengths will appear in the complementary color; thus, [CoCl4]2- (blue) absorbs light in the red region, while [Co(H2O)6]2+ (pink) absorbs light at shorter wavelengths, indicating that [CoCl4]2- has its absorption bands at longer wavelengths.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Electronic Transitions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The glycinate anion, gly-= NH2CH2CO2 -, bonds to metal ions through the N atom and one of the O atoms. Using to represent gly-, sketch the structures of the four stereoisomers of Co(gly)3.
Textbook Question
What is the oxidation state of the metal in each of the complexes?
a. [Ni(CN)5]3–
b. Ni(CO)4
c. [Co(en)2(H2O)Br]2+
d. [Cu(H2O)2(C2O4)2]2–
e. Co(NH3)3(NO2)3
Textbook Question
Draw all possible diastereoisomers of [Cr(C2O4)2(H2O)2]-. Which can exist as a pair of enantiomers?
Textbook Question
Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram for a square planar complex, and explain why square planar geometry is especially common for d8 complexes.
Textbook Question
Which of the following complexes can exist as diastereoisomers?
(a) [Cr(NH3)2Cl4]-
(b) [Co(NH3)5Br]2+
(c) [MnCl2Br2]2- (tetrahedral)
(d) [Pt(NH3)2Br2]2-