Back
BackProblem 65
Use Cramer's rule to solve each system of equations. If D = 0, then use another method to determine the solution set. See Examples 5–7.
4x + 3y = -7
2x + 3y = -11
Problem 66
Graph the solution set of each system of inequalities.
Problem 67
Use Cramer's rule to solve each system of equations. If D = 0, then use another method to determine the solution set. See Examples 5–7.
Problem 67
Find each product, if possible.
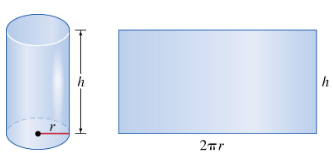
Problem 68
Solve each problem. Find the radius and height (to the nearest thousandth) of an open-ended cylinder with volume 50 in.3 and lateral surface area 65 in.2.
Problem 69
Given and , find each product, if possible. See Examples 5–7. BA
Problem 69
Use Cramer's rule to solve each system of equations. If D = 0, then use another method to determine the solution set. See Examples 5–7. 1.5
x + 3y = 5
2x + 4y = 3
Problem 69
Solve each system. (Hint: In Exercises 69–72, let 1/x = t and 1/y = u.)
2/x + 1/y = 3/2
3/x - 1/y = 1
Problem 70a
Solve each problem. The supply and demand equations for a certain commodity are given. supply: p = 2000/(2000 - q) and demand: p = (7000 - 3q)/2q.
Find the equilibrium demand.
Problem 70b
Solve each problem. The supply and demand equations for a certain commodity are given. supply: p = 2000/(2000 - q) and demand: p = (7000 - 3q)/2q.
Find the equilibrium price (in dollars).
Problem 71
Find the values of the variables for which each statement is true, if possible.
Problem 71
Given , and , find each product, if possible. See Examples 5–7. BC
- Use Cramer's rule to solve each system of equations. If D = 0, then use another method to determine the solution set. See Examples 5–7. 3x + 2y = 4 6x + 4y = 8
Problem 71
Problem 71a
Solve each problem. The supply and demand equations for a certain commodity are given. supply: p = √(0.1q + 9) - 2 and demand: p = √(25 - 0.1q).
Find the equilibrium demand.
Problem 71b
Solve each problem. The supply and demand equations for a certain commodity are given. supply: p = √(0.1q + 9) - 2 and demand: p = √(25 - 0.1q).
Find the equilibrium price (in dollars).
Problem 72
Solve each system. (Hint: In Exercises 69–72, let and .)
Problem 73
Perform each operation, if possible.
Problem 73
Given , and , find each product, if possible. See Examples 5–7. AB
Problem 73
Use Cramer's rule to solve each system of equations. If D = 0, then use another method to determine the solution set. See Examples 5–7.
(1/2)x + (1/3)y = 2
(3/2)x - (1/2)y = -12
Problem 75
Consider the following nonlinear system. Work Exercises 75 –80 in order.
y = | x - 1 |
y = x2 - 4
How is the graph of y = | x - 1 | obtained by transforming the graph of y = | x |?
Problem 75
Use Cramer's rule to solve each system of equations. If D = 0, then use another method to determine the solution set. See Examples 5–7.
2x - y + 4z = -2
3x + 2y - z = -3
x + 4y - 2z = 17
Problem 75
For what value(s) of k will the following system of linear equations have no solution? infinitely many solutions?
x - 2y = 3
-2x + 4y = k
Problem 75
Perform each operation, if possible.
Problem 77
Consider the following nonlinear system. Work Exercises 75 –80 in order.
y = | x - 1 |
y = x2 - 4
Use the definition of absolute value to write y = | x - 1 | as a piecewise-defined function.
Problem 77
Use Cramer's rule to solve each system of equations. If D = 0, then use another method to determine the solution set. See Examples 5–7.
x + 2y + 3z = 4
4x + 3y + 2z = 1
-x - 2y - 3z = 0
Problem 77
Use a system of equations to solve each problem. See Example 8. Find an equation of the line y = ax + b that passes through the points (-2, 1) and (-1, -2).
Problem 77
Perform each operation, if possible.
Problem 77
The graphs show regions of feasible solutions. Find the maximum and minimum values of each objective function. objective function = 3x + 5y
Problem 79
Perform each operation, if possible.
Problem 79
Find the maximum and minimum values of each objective function over the region of feasible solutions shown at the right. objective function = 3x + 5y