Back
BackProblem 73
Solve each equation. (5/2)x = 4/25
Problem 73
Solve each equation. Give solutions in exact form. ln(4x - 2) - ln 4 = -ln(x - 2)
Problem 74
Solve each equation. Give solutions in exact form. See Examples 5–9. ln(5 + 4x) - ln(3 + x) = ln 3
Problem 75
Solve each equation. Give solutions in exact form. See Examples 5–9. . log5 (x + 2) + log5 (x - 2) = 1
Problem 77
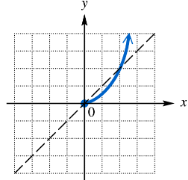
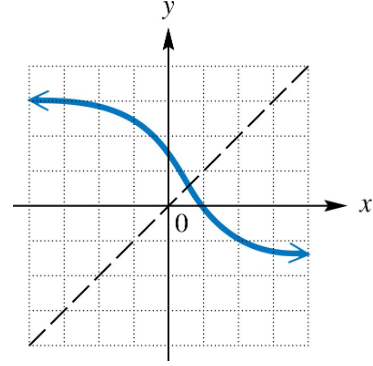
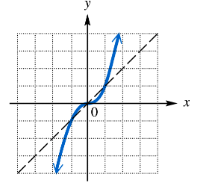
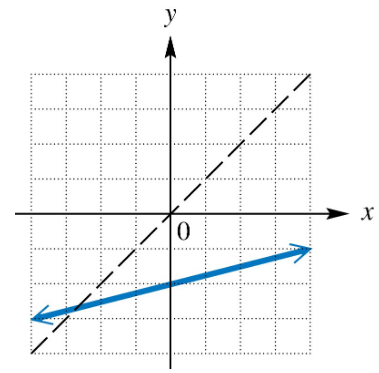
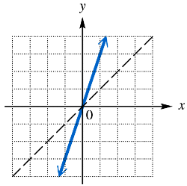
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 77
Solve each equation. Give solutions in exact form. See Examples 5–9. log2 (2x - 3) + log2 (x + 1) = 1
Problem 78
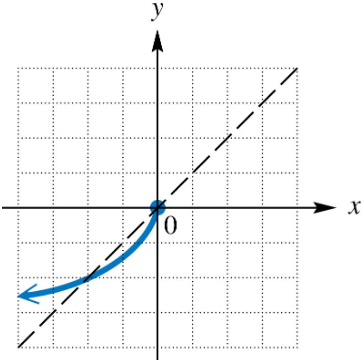
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 79
Solve each equation. Give solutions in exact form. ln ex - 2 ln e = ln e4
Problem 79
Use the change-of-base theorem to find an approximation to four decimal places for each logarithm. log2 5
Problem 79
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 80
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 81
Solve each equation. Give solutions in exact form. log2 (log2 x) = 1
Problem 81
Solve each equation. 4x-2 = 23x+3
Problem 81
Use the change-of-base theorem to find an approximation to four decimal places for each logarithm. log8 0.59
Problem 81
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 82
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 83
Solve each equation. Give solutions in exact form. log x2 = (log x)2
Problem 83
Use the change-of-base theorem to find an approximation to four decimal places for each logarithm. log1/2 3
Problem 83
Solve each equation. See Examples 4–6. x2/3 = 4
Problem 85
Use the change-of-base theorem to find an approximation to four decimal places for each logarithm. logπ e
Problem 85
Solve each equation. x5/2 = 32
Problem 87
Use the change-of-base theorem to find an approximation to four decimal places for each logarithm. log√13 12
Problem 87
Solve each equation for the indicated variable. Use logarithms with the appropriate bases. p = a + (k/ln x), for x
Problem 88
Use the change-of-base theorem to find an approximation to four decimal places for each logarithm. log√19 5
Problem 88
Solve each equation for the indicated variable. Use logarithms with the appropriate bases. r = p - k ln t, for t
Problem 91
Solve each equation. (1/e)-x = (1/e2)x+1
Problem 91
Let u = ln a and v = ln b. Write each expression in terms of u and v without using the ln function. ln (b4 √a)
Problem 91
Solve each equation for the indicated variable. Use logarithms with the appropriate bases.
Problem 92
Solve each equation for the indicated variable. Use logarithms with the appropriate bases. See Example 10. y = K/(1+ae-bx), for b
Problem 93
Let u = ln a and v = ln b. Write each expression in terms of u and v without using the ln function. ln √(a3/b5)