Back
BackProblem 85a
The equations in Exercises 79–90 combine the types of equations we have discussed in this section. Solve each equation. Then state whether the equation is an identity, a conditional equation, or an inconsistent equation. 2/x + 1/2 = 3/4
Problem 86
Solve each polynomial equation in Exercises 86–87. 2x^4 = 50 x^2
Problem 86
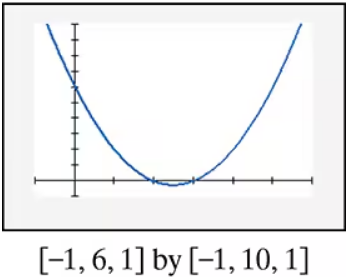
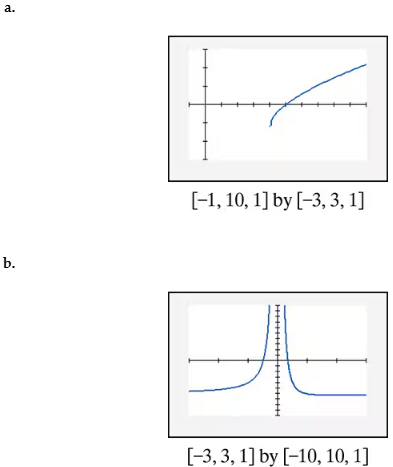
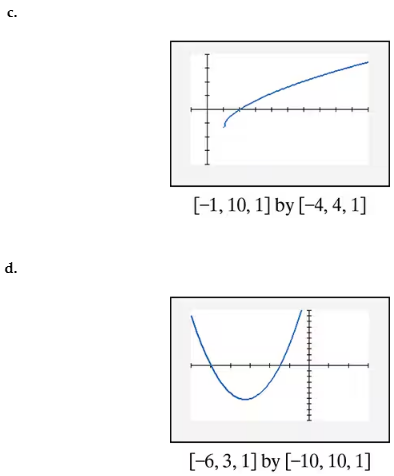
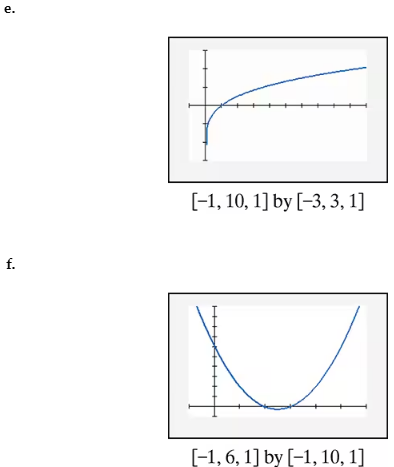
In Exercises 85–90, find the x-intercepts of the graph of each equation. Then use the x-intercepts to match the equation with its graph. [The graphs are labeled (a) through (f).]
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
Problem 87
In Exercises 59–94, solve each absolute value inequality. 5 > |4 - x|
Problem 87
Solve each equation in Exercises 83–108 by the method of your choice.
Problem 87a
The equations in Exercises 79–90 combine the types of equations we have discussed in this section. Solve each equation. Then state whether the equation is an identity, a conditional equation, or an inconsistent equation. 4/(x - 2) + 3/(x + 5) = 7/(x + 5)(x - 2)
Problem 88
Solve each radical equation in Exercises 88–89. √ (2x-3) + x = 3
Problem 88
In Exercises 85–90, find the x-intercepts of the graph of each equation. Then use the x-intercepts to match the equation with its graph. [The graphs are labeled (a) through (f).]
<Image>
Problem 89
In Exercises 59–94, solve each absolute value inequality. 1 < |2 - 3x|
Problem 89
Solve each equation in Exercises 83–108 by the method of your choice.
Problem 89a
The equations in Exercises 79–90 combine the types of equations we have discussed in this section. Solve each equation. Then state whether the equation is an identity, a conditional equation, or an inconsistent equation. 4x/(x + 3) - 12/(x - 3) = (4x2 + 36)/(x2 - 9)
Problem 90
In Exercises 85–90, find the x-intercepts of the graph of each equation. Then use the x-intercepts to match the equation with its graph. [The graphs are labeled (a) through (f).] y = 2(x + 2)^2 + 5(x + 2) - 3
Problem 90a
The equations in Exercises 79–90 combine the types of equations we have discussed in this section. Solve each equation. Then state whether the equation is an identity, a conditional equation, or an inconsistent equation. 4/(x2 + 3x - 10) - 1/(x2 + x - 6) = 3/(x2 - x - 12)
Problem 91
In Exercises 59–94, solve each absolute value inequality.
Problem 91a
Solve each equation in Exercises 83–108 by the method of your choice. (2x + 3)(x + 4) = 1
Problem 92
Solve each equation in Exercises 92–93 by making an appropriate substitution. x^4 - 5x^2 + 4 = 0
Problem 92
In Exercises 91–100, find all values of x satisfying the given conditions. y = |2 - 3x| and y = 13
Problem 92
Solve each equation in Exercises 83–108 by the method of your choice. (2x - 5)(x + 1) = 2
Problem 93
Solve each equation in Exercises 83–108 by the method of your choice. (3x - 4)2 = 16
Problem 93a
Solve each absolute value inequality. 4 + |3 - x/3| ≥ 9
Problem 94
Solve the equations containing absolute value in Exercises 94–95. |2x+1| = 7
Problem 94
In Exercises 91–100, find all values of x satisfying the given conditions.
Problem 95
In Exercises 95–102, use interval notation to represent all values of x satisfying the given conditions.
Problem 95
In Exercises 95–99, perform the indicated operations and write the result in standard form. 4/(2 + i)(3 - i)
Problem 95
Solve each equation in Exercises 83–108 by the method of your choice.
Problem 95a
Evaluate x2 - x for the value of x satisfying 4(x - 2) + 2 = 4x - 2(2 - x).
Problem 96
In Exercises 91–100, find all values of x satisfying the given conditions. and
Problem 96
Solve each equation in Exercises 83–108 by the method of your choice.
Problem 96
Perform the indicated operations and write the result in standard form. (1 + i)/(1 + 2i) + (1 - i)/(1 - 2i)
Problem 96a
Use interval notation to represent all values of x satisfying the given conditions. y1 = (2/3)(6x - 9) + 4, y2 = 5x + 1, and y1 > y2