Explain why continuous growth enhances the phenomenon known as phenotypic plasticity.

Identify the structure you are consuming when you eat each of the following: Asparagus, Brussels sprouts, celery, spinach, carrots, and potatoes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Plant Anatomy
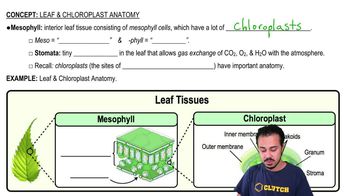
Vegetative Structures

Botanical Classification
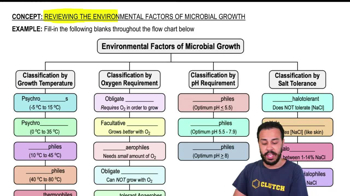
What does the cuticle do?
What do stomata do?
Predict how the thickness of the cuticle and the number of stomata differ in plants from wet habitats versus dry habitats.
You attached a birdfeeder to a tree 5 years ago at a position 6 feet above the ground. The tree has grown since at a rate of 1 foot per year. What is the current height of the birdfeeder?
Trees can be killed by girdling—the removal of bark and vascular cambium in a ring all the way around the tree. Explain why.
Plants experience a vast array of conditions that can alter their growth and development, including temperature and availability of water, nutrients, and light. They are also exposed to pollutants such as acid rain formed largely as a result of burning fossil fuels and volcanic eruptions. Acid rain can strip minerals and nutrients from the soil and eat away the outer waxy layer of tissue that protects a plant. Acid rain is still a major environmental problem in certain regions.
How does acid rain affect plant growth?
Develop a hypothesis on the likely effects of acid rain on primary growth in trees.
Based on your hypothesis, make some predictions about the impact of acid rain on the height of tree trunks.
Plants experience a vast array of conditions that can alter their growth and development, including temperature and availability of water, nutrients, and light. They are also exposed to pollutants such as acid rain formed largely as a result of burning fossil fuels and volcanic eruptions. Acid rain can strip minerals and nutrients from the soil, and eat away the outer waxy layer of tissue that protects a plant. Acid rain is still a major environmental problem in certain regions. How does acid rain affect plant growth? Researchers tested the effects of acid rain (pH 2.0) on seedlings of two different species, camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora) and chinaberry tree (Melia azederach), using distilled water as a control. Results of the experiments are shown here. Note that acid rain caused a significant reduction of growth in chinaberry trees (*** means P < 0.001), but not in camphor trees. What was the approximate percentage of growth reduction observed in the chinaberry trees treated with acid rain?
