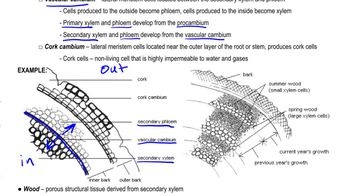
Which statement best characterizes primary growth?
a. It does not occur in roots, only in shoots.
b. It leads to the development of cork tissue.
c. It produces the dermal, ground, and vascular tissues.
d. It produces rings of xylem, phloem, and cork tissue.