Why is it ecologically significant that animals are heterotrophic and multicellular?

Suppose that a gene originally identified in nematodes (roundworms) is found to be homologous with a gene that can cause developmental abnormalities in humans. Would it be possible to use fruit flies as a model organism to study this gene? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
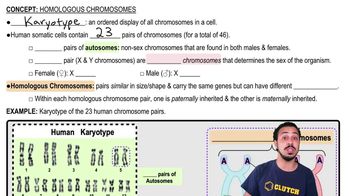
Homologous Genes
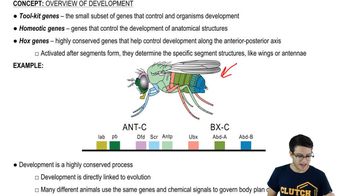
Model Organisms
Developmental Biology
To estimate the relative abundance of the major phyla, calculate how many named species of arthropods, mollusks, and nematode worms exist per named species of chordate (the phylum containing vertebrates, including humans; see Table 30.1).
Do you think these calculations are likely to be underestimates or overestimates? Why?
Evaluate this statement: Animals evolved from simple to complex.
The vast majority of animals that ever existed are now extinct, but Tereza Jezkova and John Wiens wondered which variables were most important in driving the diversification of species that exist today.
Why are there so many species in some phyla, such as Cnidaria (see photo), but so few in others, such as Ctenophora?
Draw a horizontal axis to represent the number of species within phyla using a logarithmic scale (1, 10, 100, 1000 species, etc.). Then use Table 30.1 to map seven representative phyla from small to large at intervals of about an order of magnitude on this scale.
