Heartwood and sapwood consist of
a. Bark
b. Periderm
c. Secondary xylem
d. Secondary phloem

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


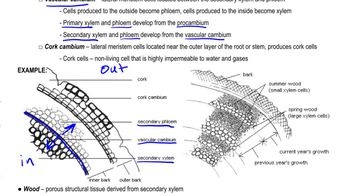
Heartwood and sapwood consist of
a. Bark
b. Periderm
c. Secondary xylem
d. Secondary phloem
The phase change of an apical meristem from the juvenile to the mature vegetative phase is often revealed by
a. A change in the morphology of the leaves produced
b. The initiation of secondary growth
c. The formation of lateral roots
d. The activation of floral meristem identity genes
The vascular cambium gives rise to
a. All xylem
b. All phloem
c. Primary xylem and phloem
d. Secondary xylem and phloem
Root apical meristems are found
a. Only in taproots.
b. Only in lateral roots.
c. Only in adventitious roots.
d. In all roots.
Suppose a flower had normal expression of genes A and C and expression of gene B in all four whorls. Based on the ABC hypothesis, what would be the structure of that flower, starting at the outermost whorl?
a. Carpel-petal-petal-carpel
b. Petal-petal-stamen-stamen
c. Sepal-carpel-carpel-sepal
d. Sepal-sepal-carpel-carpel
Which of the following arise(s), directly or indirectly, from meristematic activity?
a. Secondary xylem
b. Leaves
c. Dermal tissue
d. All of the above