The root pericycle is the site where
a. Secondary growth originates.
b. Root hairs originate.
c. Lateral roots originate.
d. The endodermis originates.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
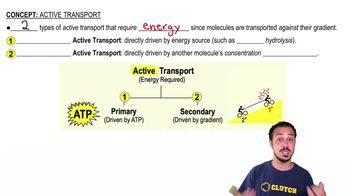
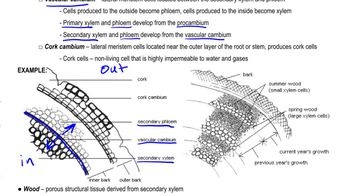

The root pericycle is the site where
a. Secondary growth originates.
b. Root hairs originate.
c. Lateral roots originate.
d. The endodermis originates.
Root apical meristems are found
a. Only in taproots.
b. Only in lateral roots.
c. Only in adventitious roots.
d. In all roots.
Suppose a flower had normal expression of genes A and C and expression of gene B in all four whorls. Based on the ABC hypothesis, what would be the structure of that flower, starting at the outermost whorl?
a. Carpel-petal-petal-carpel
b. Petal-petal-stamen-stamen
c. Sepal-carpel-carpel-sepal
d. Sepal-sepal-carpel-carpel
A strawberry plant mutant that fails to make stolons would suffer from
a. Too little mineral absorption.
b. A tendency to topple over.
c. Too little water absorption.
d. A reduction in asexual reproduction