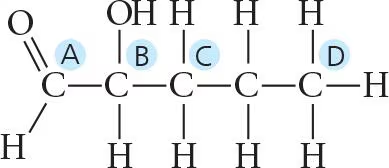Back
BackProblem 1
Organic chemistry is currently defined as
a. The study of compounds made only by living cells.
b. The study of carbon compounds.
c. The study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
d. The study of hydrocarbons.
Problem 2
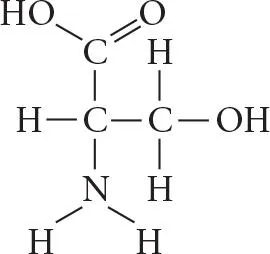
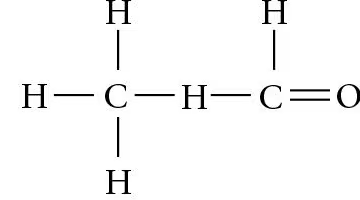
Which functional group is present in this molecule?
A.sulfhydryl
B.carboxyl
C.methyl
D.phosphate
Problem 3
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base?
a. Hydroxyl
b. Carbonyl
c. Amino
d. Phosphate
Problem 4
Visualize the structural formula of each of the following hydrocarbons. Which hydrocarbon has a double bond in its carbon skeleton?
a. C3H8
b. C₂H₆
c. C₂H₄
d. C₂H₂
Problem 5
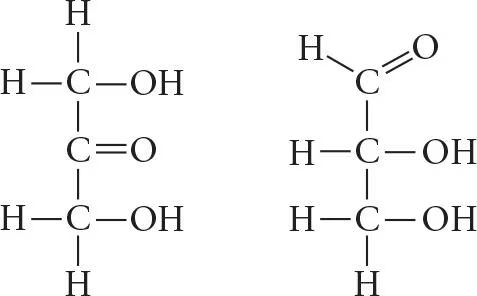
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between these two sugar molecules:
a. Structural isomers
b. Cis-trans isomers
c. Enantiomers
d. Isotopes
Problem 6
Identify the asymmetric carbon in this molecule:
Problem 7
Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
a. The replacement of the —OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
b. The addition of a thiol to a hydroxyl
c. The addition of a hydroxyl to a phosphate
d. The replacement of the nitrogen of an amine with oxygen
Problem 8
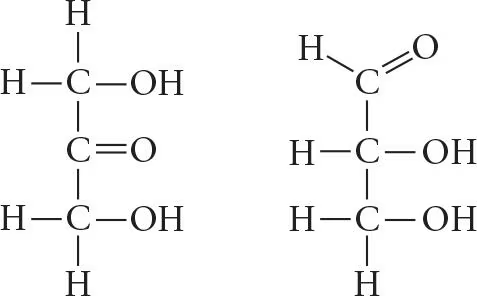
Which of the molecules shown in question 5 has an asymmetric carbon? Which carbon is asymmetric?
Problem 9b
Draw Lewis dot structures for each hypothetical molecule shown below, using the correct number of valence electrons for each atom. Determine which molecule makes sense because each atom has a complete valence shell, and each bond has the correct number of electrons. Explain what makes the other molecule nonsensical, considering the number of bonds each type of atom can make.