Which of the following is true of a codon?
a. It never codes for the same amino acid as another codon.
b. It can code for more than one amino acid.
c. It can be either in DNA or in RNA
d. It is the basic unit of protein structure

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
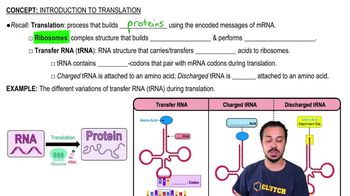
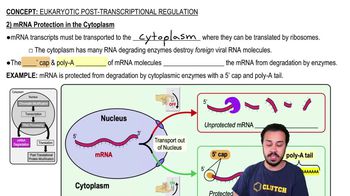
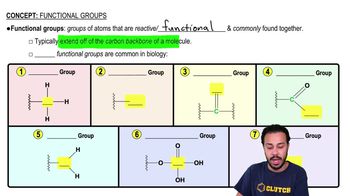
Which of the following is true of a codon?
a. It never codes for the same amino acid as another codon.
b. It can code for more than one amino acid.
c. It can be either in DNA or in RNA
d. It is the basic unit of protein structure
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until
a. The two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter.
b. Several transcription factors have bound to the promoter.
c. The 5′ caps are removed from the mRNA.
d. The DNA introns are removed from the template.
Which of the following is true of RNA processing? (A) Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus. (B) Nucleotides are added at both ends of the RNA. (C) Ribozymes may function in the addition of a 5′ cap. (D) RNA splicing adds a poly-A tail to the mRNA.
Which component is directly involved in translation?
A. RNA polymerase
B. ribosome
C. spliceosome
D. DNA
Using Figure 17.6, identify a 5′→3′ sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
a. 5′-UUUCCCAAA-3′
b. 5′-GAACCCCTT-3′
c. 5′-CTTCGGGAA-3′
d. 5′-AAACCCUUU-3′