6. Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics
Specificity Constant
Practice this topic
- Open Question
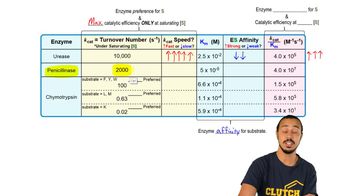
Use the data in the chart below to provide answers to the following problems:
A) List the substrates from most preferred to least preferred under physiological conditions.
a) B, A, C. b) C, B, A. c) B, C, A. d) A, C, B.
B) List the substrates from most preferred to least preferred under saturating [S].
a) B, A, C. b) C, B, A. c) B, C, A. d) A, C, B.
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following options is correct concerning the turnover number (k cat) and the specificity constant?
- Open Question
Use the Lineweaver-Burk plot to help you calculate the Vmax, kcat, Km and specificity constant for the enzyme.
Assume the [E]T = 2.9 nM. Hint: Pay close attention to units.
Vmax = ___________.
kcat = ___________.
Km = ___________.
kcat / Km = ___________.
- Open Question
Explain the steps you could take to accurately find the K m, Vmax, and specificity constant for an enzyme from the following kinetic data, assuming the experiments were all done with [E]T = 0.1 mM.
Step #1: ___________________________________________
Step #2: ___________________________________________
Step #3: ___________________________________________
Step #4: ___________________________________________
Step #5: ___________________________________________
- Multiple Choice
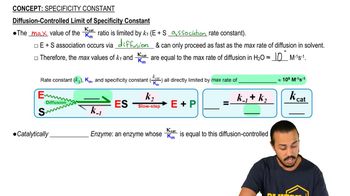
The specificity constant is obtained at low [S] via variable substitution into the Michaelis-Menten equation (Vmax = kcat[E]T). Considering this about the MM-equation, what is the relationship between changes in [S] & V0 when the [S] is super small and well below the Km?