Back
Back Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition
Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition Ch. 6 Bones and Bone Structure
Ch. 6 Bones and Bone StructureProblem 1
Blood cell formation occurs in:
(a) Yellow bone marrow
(b) Red bone marrow
(c) The matrix of bone tissue
(d) The ground substance of bones
Problem 2
Two-thirds of the weight of bone is accounted for by:
(a) Crystals of calcium phosphate
(b) Collagen fibers
(c) Osteocytes
(d) Calcium carbonate
Problem 3
The membrane found wrapping the bones, except within the joint cavity, is the:
(a) Periosteum
(b) Endosteum
(c) Perforating fibers
(d) A, b, and c are correct
Problem 4
The basic functional unit of compact bone is the Haversian system or:
(a) Osteocyte
(b) Osteoclast
(c) Osteon
(d) Osseous matrix
(e) Osseous lamellae
Problem 5
The vitamins essential for normal adult bone maintenance and repair are:
(a) A and E
(b) C and D3
(c) B and E
(d) B complex and K
Problem 6
The hormones that coordinate the storage, absorption, and excretion of calcium ions are:
(a) Growth hormone and thyroxine
(b) Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone
(c) Calcitriol and cholecalciferol
(d) Estrogens and androgens
Problem 7a
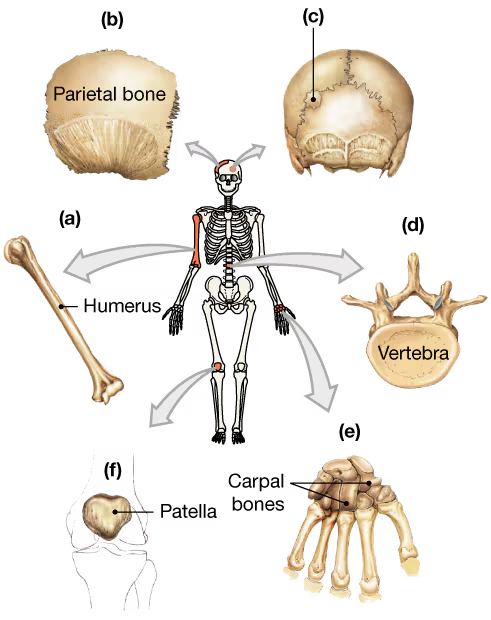
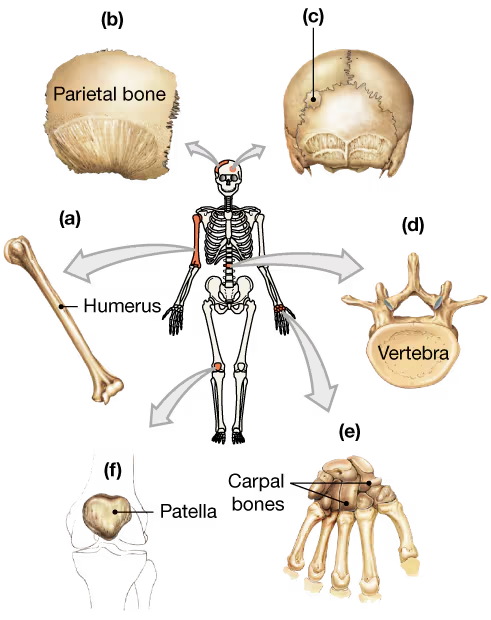
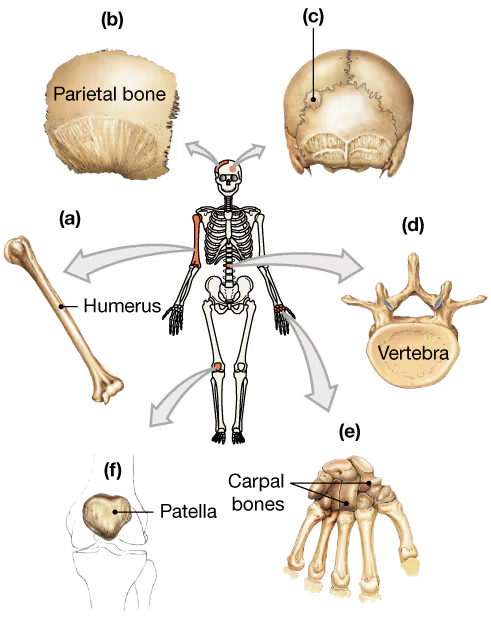
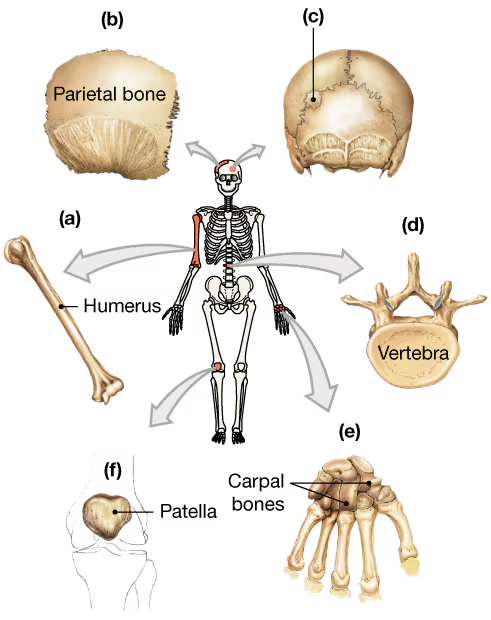
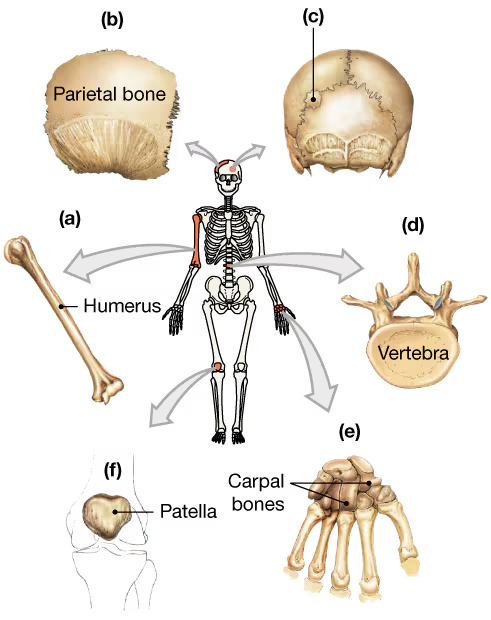
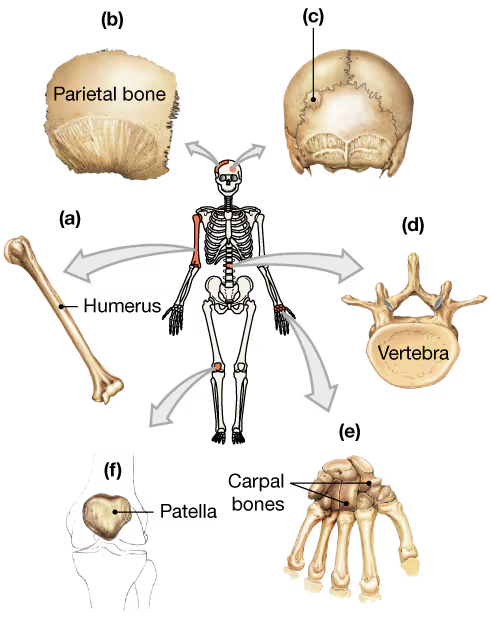
Classify the bones in the following diagram according to their shape.
a. _____
Problem 7b
Classify the bones in the following diagram according to their shape.
b. _____
Problem 7c
Classify the bones in the following diagram according to their shape.
c. _____
Problem 7d
Classify the bones in the following diagram according to their shape.
d. _____
Problem 7e
Classify the bones in the following diagram according to their shape.
e. _____
Problem 7f
Classify the bones in the following diagram according to their shape.
f. _____
Problem 8
The presence of an epiphyseal line indicates:
(a) Epiphyseal growth has ended
(b) Epiphyseal growth is just beginning
(c) Growth of bone diameter is just beginning
(d) The bone is fractured at the location
(e) No particular event
Problem 9
The primary reason that osteoporosis accelerates after menopause in women is:
(a) Reduced levels of circulating estrogens
(b) Reduced levels of vitamin C
(c) Diminished osteoclast activity
(d) Increased osteoblast activity
Problem 10
The nonpathologic loss of bone that occurs with aging is called:
(a) Osteomyelitis
(b) Osteoporosis
(c) Osteopenia
(d) Osteitis
(e) Osteomalacia
Problem 11
Name the major functions of the skeletal system.
Problem 12
List the four distinctive cell populations of bone tissue.
Problem 13
What are the primary parts of a typical long bone?
Problem 14
What is the primary difference between endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification?
Problem 15
List the organic and inorganic components of bone matrix.
Problem 16a
What nutritional factors are essential for normal bone growth and maintenance?
Problem 16b
What hormonal factors are necessary for normal bone growth and maintenance?
Problem 17
Which three organs or tissues interact to assist in the regulation of calcium ion concentration in body fluids?
Problem 18
What are the major effects of parathyroid hormone?
Problem 19
If spongy bone has no osteons, how do nutrients reach the osteocytes?
Problem 20
Why are stresses or impacts to the side of the shaft in a long bone more dangerous than stress applied to the long axis of the shaft?
Problem 21
Why do extended periods of inactivity cause degenerative changes in the skeleton?
Problem 22
What are the functional relationships between the skeleton, on the one hand, and the digestive and urinary systems, on the other?
Problem 23
Why would a physician be concerned about the growth patterns of a young child request an x-ray of the hand?
Problem 24
Why does a second fracture in the same bone tend to occur at a site different from that of the first fracture?