Back
Back Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition
Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition Ch. 5 The Integumentary System
Ch. 5 The Integumentary SystemProblem 1a
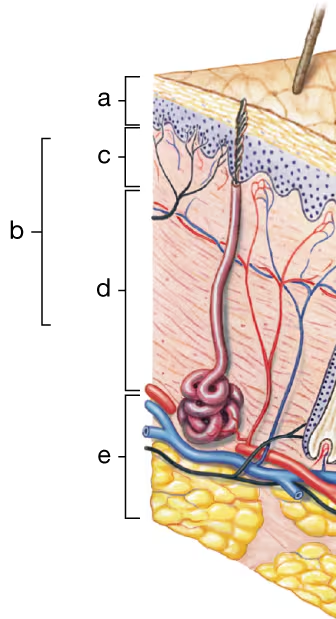
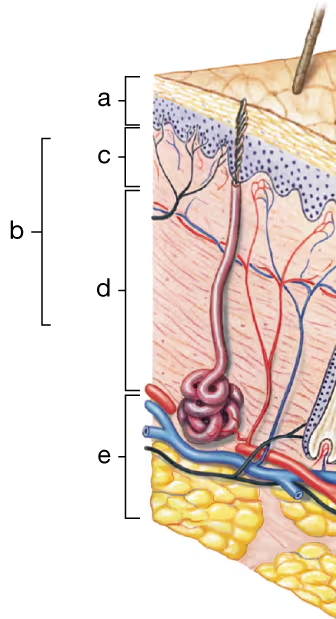
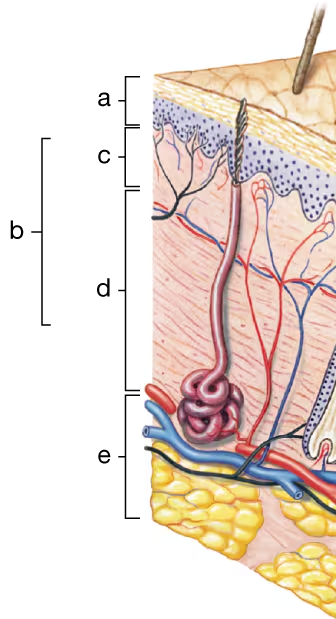
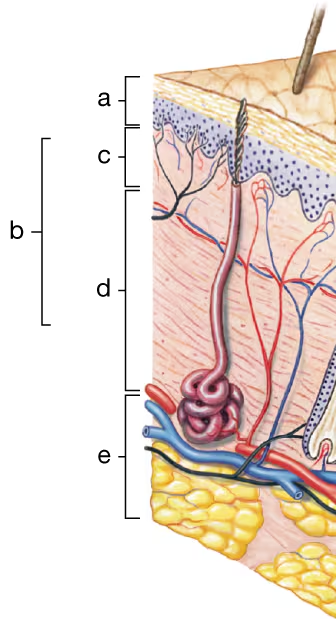
Identify the different portions (a–d) of the cutaneous membrane and the underlying layer of loose connective tissue (e) in the diagram to the right.
a. ____
Problem 1b
Identify the different portions (a–d) of the cutaneous membrane and the underlying layer of loose connective tissue (e) in the diagram to the right.
b. ____
Problem 1c
Identify the different portions (a–d) of the cutaneous membrane and the underlying layer of loose connective tissue (e) in the diagram to the right.
c. ____
Problem 1d
Identify the different portions (a–d) of the cutaneous membrane and the underlying layer of loose connective tissue (e) in the diagram to the right.
d. ____
<IMAGE>
Problem 1e
Identify the different portions (a–d) of the cutaneous membrane and the underlying layer of loose connective tissue (e) in the diagram to the right.
e. ____
Problem 2
The two major components of the integumentary system are
(a) The cutaneous membrane and the accessory structures
(b) The epidermis and the subcutaneous layer
(c) The hair and the nails
(d) The dermis and the subcutaneous layer
Problem 3
Beginning at the basement membrane and traveling toward the free surface, the epidermis includes the following strata:
(a) Corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, basale
(b) Granulosum, lucidum, spinosum, basale, corneum
(c) Basale, spinosum, granulosum, lucidum, corneum
(d) Lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, basale, corneum
Problem 6
The two major components of the dermis are the
(a) Superficial fascia and cutaneous membrane
(b) Epidermis and subcutaneous layer
(c) Papillary layer and reticular layer
(d) Stratum basale and stratum corneum
Problem 7
The cutaneous plexus and subpapillary plexus consist of
a. Blood vessels providing the dermal blood supply.
b. A network of nerves providing dermal sensations.
c. Specialized cells for cutaneous sensations.
d. Gland cells that release cutaneous secretions.
Problem 15
In which layer(s) of the epidermis does cell division occur?
Problem 17
What widespread effects does epidermal growth factor (EGF) have on the integument?
Problem 18
What two major layers constitute the dermis, and what components are in each layer?
Problem 19
List the four phases in the regeneration of the skin after an injury.
Problem 21
In clinical practice, drugs can be delivered by diffusion across the skin. This delivery method is called transdermal administration. Why are fat-soluble drugs more suitable for transdermal administration than drugs that are water soluble?
Problem 23
Why is it important for a surgeon to choose—when possible—an incision pattern according to the skin's tension lines?
Problem 24
The fibrous protein that is responsible for the strength and water resistance of the skin surface is
(a) Collagen
(b) Eleidin
(c) Keratin
(d) Elastin
(e) Keratohyalin
Problem 29a
Exposure to optimum amounts of sunlight is necessary for proper bone maintenance and growth in children.
(a) What does sunlight do to promote bone maintenance and growth?