Back
Back Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition
Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition Ch. 7 The Axial Skeleton
Ch. 7 The Axial SkeletonProblem 1
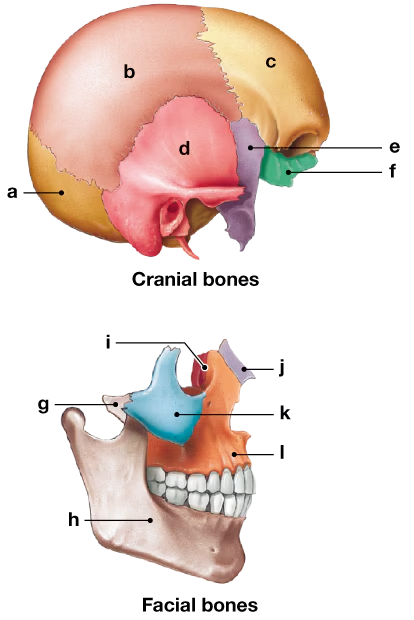
Identify the cranial and facial bones in the diagram below.
a. ___
b. ___
c. ___
d. ___
e. ___
f. ___
g. ___
h. ___
i. ___
j. ___
k. ___
l. ___
Problem 2
Which of the following lists contains only facial bones? (a) mandible, maxilla, nasal, zygomatic, (b) frontal, occipital, zygomatic, parietal, (c) occipital, sphenoid, temporal, lacrimal, (d) frontal, parietal, occipital, sphenoid.
Problem 3
The unpaired facial bones include the:
(a) Lacrimal and nasal
(b) Vomer and mandible
(c) Maxilla and mandible
(d) Zygomatic and palatine
Problem 4
The boundaries between skull bones are immovable joints called:
(a) Foramina
(b) Fontanelles
(c) Lacunae
(d) Sutures
Problem 5
The joint between the frontal and parietal bones is correctly called the ____ suture.
(a) Parietal
(b) Lambdoid
(c) Squamous
(d) Coronal
Problem 6
Blood vessels that drain blood from the head pass through the:
(a) Jugular foramina
(b) Hypoglossal canals
(c) Stylomastoid foramina
(d) Mental foramina
(e) Lateral canals
Problem 7
or each of the following vertebrae, indicate its vertebral region. a. ____ b. ____ c. ____
Problem 11
Which eight bones make up the cranium?
Problem 12
What seven bones constitute the orbital complex?
Problem 15
What is the relationship between the temporal bone and the ear?
Problem 16
What is the relationship between the ethmoid and the nasal cavity?