Back
Back Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition
Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition Ch. 4 The Tissue Level of Organization
Ch. 4 The Tissue Level of OrganizationProblem 1a
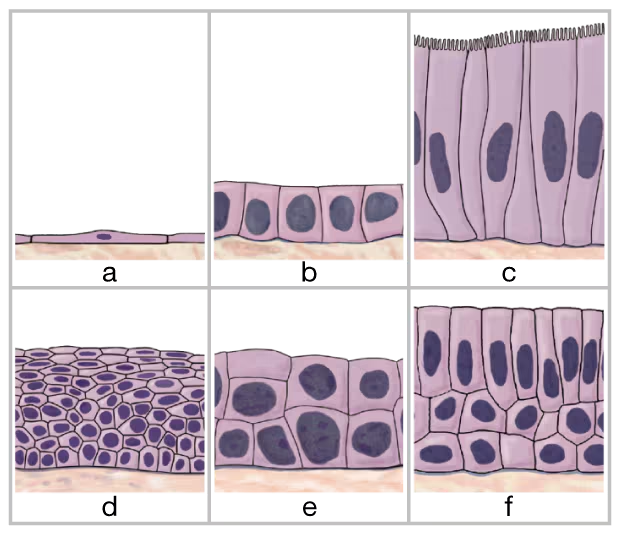
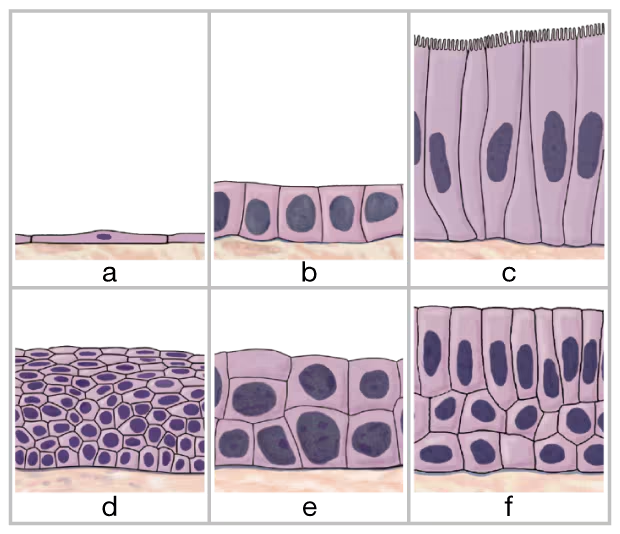
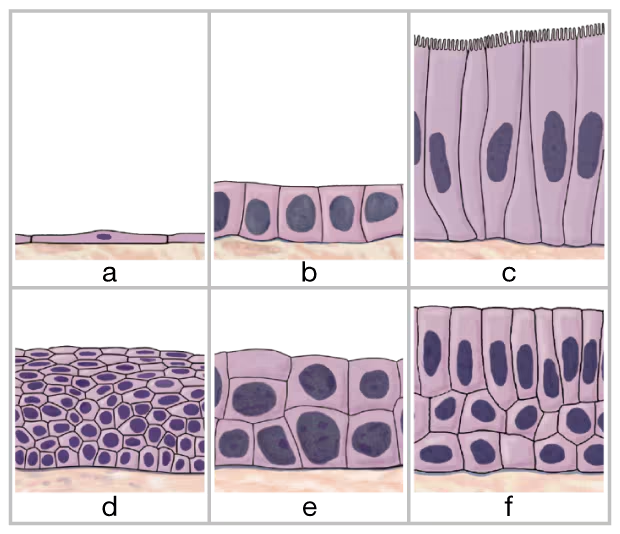
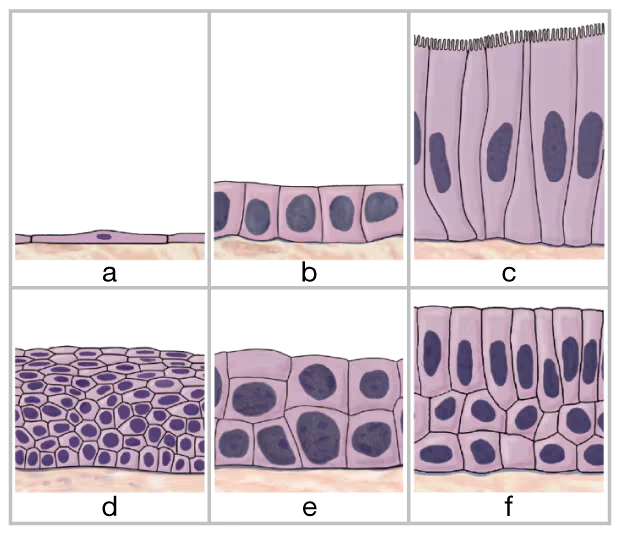
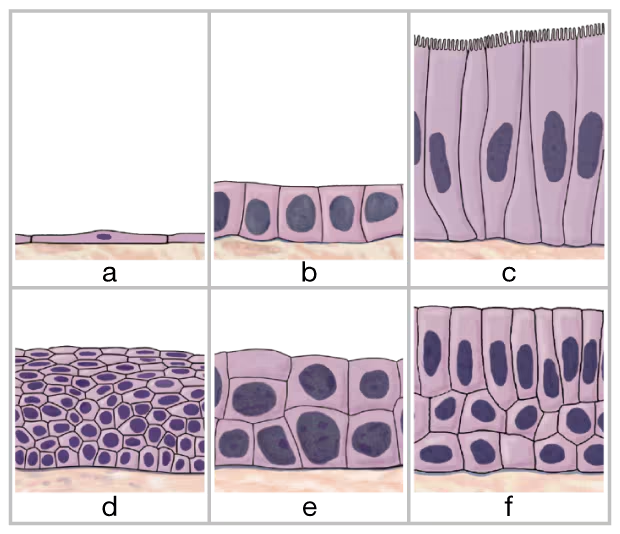
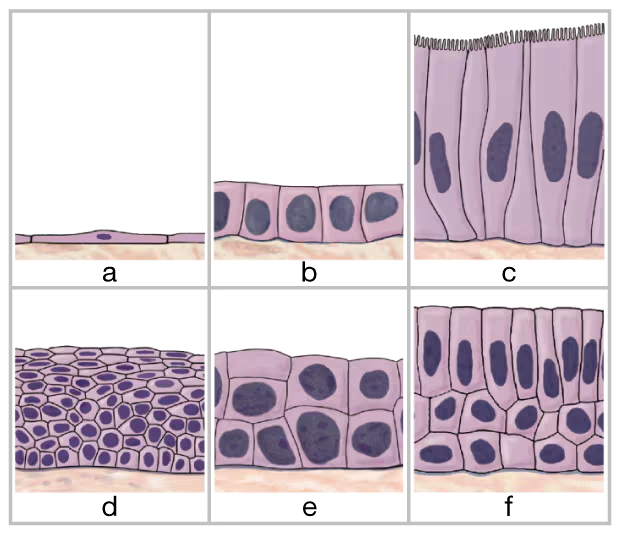
Identify the six types of epithelial tissue shown in the drawing below.
a. __
Problem 1b
Identify the six types of epithelial tissue shown in the drawing below.
b. ___
Problem 1c
Identify the six types of epithelial tissue shown in the drawing below.
c. ___
Problem 1d
Identify the six types of epithelial tissue shown in the drawing below.
d. ___
Problem 1e
Identify the six types of epithelial tissue shown in the drawing below.
e. ___
Problem 1f
Identify the six types of epithelial tissue shown in the drawing below.
f. ___
Problem 2
Collections of specialized cells and cell products that perform a relatively limited number of functions are called
(a) Cellular aggregates,
(b) Tissues
(c) Organs
(d) Organ systems
(e) Organisms
Problem 3
Tissue that is specialized for contraction is
(a) Epithelial tissue
(b) Muscle tissue
(c) Connective tissue
(d) Nervous tissue
Problem 4
A type of cell junction common in cardiac and smooth muscle tissues is the
(a) Hemidesmosome
(b) Basal junction
(c) Tight junction
(d) Gap junction
Problem 5
The most abundant connections between cells in the superficial layers of the skin are
(a) Connexons
(b) Gap junctions
(c) Desmosomes
(d) Tight junctions
Problem 8
Matrix is a characteristic of which type of tissue?
(a) Epithelial
(b) Nervous
(c) Muscle
(d) Connective
Problem 9
Which of the following epithelia most easily permits diffusion?
(a) Stratified squamous
(b) Simple squamous
(c) Transitional
(d) Simple columnar
Problem 10
Functions of connective tissue include
(a) Establishing a structural framework for the body
(b) Storing energy reserves
(c) Providing protection for delicate organs
(d) All of these
(e) a and c only.
Problem 11
The three major types of cartilage in the body are
(a) Collagen, reticular, and elastic
(b) Areolar, adipose, and reticular
(c) Hyaline, elastic, and fibrous
(d) Tendons, reticular, and elastic
Problem 13
The type of cartilage growth characterized by adding new layers of cartilage to the surface is
(a) Interstitial growth
(b) Appositional growth
(c) Intramembranous growth
(d) Longitudinal growth.
Problem 15
Axons, dendrites, and a cell body are characteristic of cells located in
(a) Nervous tissue
(b) Muscle tissue
(c) Connective tissue
(d) Epithelial tissue
Problem 17
What are the four essential functions of epithelial tissue?
Problem 20
List three basic components of connective tissues.
Problem 22
What two cell populations make up nervous tissue? What is the function of each?
Problem 25
Describe the fluid connective tissues in the human body. What are the main differences between fluid connective tissues and supporting connective tissues?
Problem 27
A layer of glycoproteins and a network of fine protein filaments that prevents the movement of proteins and other large molecules from the connective tissue to the epithelium describe
(a) Interfacial canals
(b) The basement membrane
(c) The reticular lamina
(d) Areolar tissue
(e) Squamous epithelium
Problem 28
Why does damaged cartilage heal slowly?
(a) Chondrocytes cannot be replaced if killed, and other cell types must take their place.
(b) Cartilage is avascular, so nutrients and other molecules must diffuse to the site of injury.
(c) Damaged cartilage becomes calcified, thus blocking the movement of materials required for healing.
(d) Chondrocytes divide more slowly than other cell types, delaying the healing process.
(e) Damaged collagen cannot be quickly replaced, thereby slowing the healing process.
Problem 29
List the similarities and differences among the three types of muscle tissue.
Problem 31
During a lab practical, a student examines a tissue that is composed of densely packed protein fibers that run parallel to each other and form a cord. There are no striations, but small nuclei are visible. The student identifies the tissue as skeletal muscle. Why is the student's choice wrong, and what tissue is he probably observing?